Methylmalonyl-CoA
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
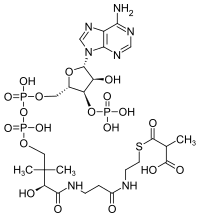
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Methylmalonyl-CoA | ||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 25 H 40 N 7 O 19 P 3 S | ||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 867.6 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Methylmalonyl-Coenzyme A , or methylmalonyl-CoA for short , is an organic chemical compound . It is a thioester - made from coenzyme A and methylmalonic acid - and a carboxylic acid . In biochemistry , the anion of the carboxylic acid is also known as methylmalonyl-CoA . The thioester occurs as an intermediate product in the breakdown of fatty acids with an odd number of carbon atoms and some amino acids . The product succinyl-CoA formed during the breakdown of methylmalonyl-CoA is also formed in the metabolism in the citric acid cycle ; the reaction with guanosine diphosphate ( GDP ) and free phosphate is catalyzed by the succinyl-CoA synthetase and produces the energy-rich guanosine triphosphate ( GTP ) , which is analogous to ATP .
Significance in fatty acid and amino acid metabolism
Methylmalonyl-CoA is produced in the body when propionyl-CoA , which is formed from fatty acids with an odd number of carbon atoms, is converted into succinyl-CoA, which reacts further in the citric acid cycle. The formation reaction from propionyl-CoA is catalyzed by propionyl-CoA carboxylase in a biotin- dependent carboxylation . First the D- enantiomer is formed . The methylmalonyl-CoA racemase catalyzes the isomerization of D-methylmalonyl-CoA to L-methylmalonyl-CoA. This intermediate product is converted to succinyl-CoA by the L-methylmalonyl-CoA mutase . The reaction requires vitamin B 12 as a cofactor.
When some amino acids such as isoleucine , valine , methionine and threonine are broken down , propionyl-CoA is also formed, which is converted to succinyl-CoA via methylmalonyl-CoA in the same way as fatty acids.
Pathobiochemistry
A deficiency in L-methylmalonyl-CoA mutase or a pronounced vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to methylmalonic aciduria , which leads to toxic effects via an accumulation of methylmalonyl-CoA. If left untreated, the disease can quickly lead to severe brain damage or death.
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ A b H. Robert Horton, Laurence A. Moran, K. Gray Scrimgeour, J. David Rawn, Marc D. Perry: Biochemistry. 4th Edition, Pearson Education, 2008, ISBN 978-3-8273-7312-0 , pp. 674-675.
- ^ A b c R. Witkowski, O. Prokop, E. Ullrich: Lexicon of syndromes and malformations: causes, genetics, risks. 7th edition, Springer, 2003, ISBN 978-3-540-44305-6 , p. 818.
literature
- G. Löffler, PE Petrides, P. C: Heinrich: Biochemistry and Pathobiochemistry . 8th edition, Springer, Heidelberg 2006, ISBN 978-3-540-32680-9 .