Molybdenum (V) fluoride
| Crystal structure | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||
| __ Mon 5+ __ F - | |||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Molybdenum (V) fluoride | ||||||||||||
| other names |
Molybdenum pentafluoride |
||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | MoF 5 | ||||||||||||
| Brief description |
yellow solid |
||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 190.94 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||
| density |
3.5 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||
| Melting point |
45 ° C |
||||||||||||
| boiling point |
212 ° C |
||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Molybdenum (V) fluoride is an inorganic chemical compound of molybdenum from the group of fluorides .
Extraction and presentation
Molybdenum (V) fluoride can be obtained by reacting molybdenum hexacarbonyl with fluorine at −78 ° C.
Alternatively, the representation is made by reacting elemental molybdenum with molybdenum (VI) fluoride at 60 ° C with a yield of 75 - 80%:
properties
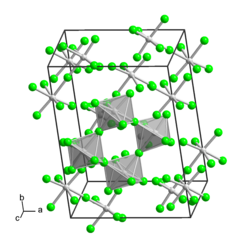
Molybdenum (V) fluoride is a yellow, hydrolysis-sensitive solid that smokes in the air. Its crystal structure can be described as a cyclic tetramer [MoF 5 ] 4 made of distorted octahedra. It is the namesake of the MoF 5 structure type.
The melting temperature of over 60 ° C given in the literature contradicts more recent values of about 45 ° C determined both thermographically and visually in a thin-walled quartz capillary. The lack of a full chemical analysis in the older sources suggests the presence of admixtures of molybdenum (VI) oxide fluoride MoOF 4 (melting point 98 ° C) in the synthesized preparations, which can significantly increase the melting point.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Georg Brauer , with the assistance of Marianne Baudler a . a. (Ed.): Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry . 3rd, revised edition. tape I . Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1975, ISBN 3-432-02328-6 , pp. 266 .
- ↑ a b web elements: Periodic Table of the Elements | Molybdenum | tetramolybdenum_eicosafluoride
- ↑ a b ya. V. Vasil'ev, AA Opalovskii, KA Khaldoyanidi: Magnetic properties of molybdenum pentafluoride. In: Bulletin of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR Division of Chemical Science. 18, 1969, p. 231, doi : 10.1007 / BF00905525 .
- ↑ a b c T. J. Ouellette et al .: Molybdenum (V) fluoride (Molybdenum pentalfluoride) . In: FA Cotton (Ed.): Inorganic Syntheses . tape 13 . McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc., 1972, ISBN 07-013208-9 ( defective ) , p. 146-1150 (English).
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ AJ Edwards, RD Peacock, RWH Small: The Preparation and Structure of Molybdenum Pentafluoride . In: J. Chem. Soc. 1962, p. 4486-4491 .
- ^ Ralph F. Krause, Thomas B. Douglas: The melting temperature, vapor density, and vapor pressure of molybdenum pentafluoride. In: The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics. 9, 1977, p. 1149, doi : 10.1016 / 0021-9614 (77) 90116-1 .

![{\ displaystyle {\ ce {Mon + 5 MoF6 -> [T] [] 6 MoF5}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d1b806b66b3af8d451dface9977cdc679d84ea78)