Molybdocene dichloride
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
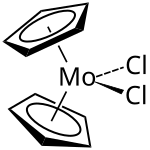
|
||||||||||||||||
| Crystal system |
monoclinic |
|||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Dichlorobis (η 5 -cyclopentadienyl) molybdenum (IV) | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 10 Cl 2 Mo | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
gray or green solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 297.04 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
Decomposes in water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Molybdocene dichloride or, according to the IUPAC nomenclature, dichlorobis ( η 5 - cyclopentadienyl ) molybdenum (IV) , is an organometallic compound from the metallocenes family . The crystalline, moisture-sensitive solid, described as dark green or gray depending on the literature, is used in the laboratory for the production of other molybdocene derivatives.
Extraction and presentation
Molybdocene dichloride was first reported in 1967 by Malcolm LH Green and L. Cooper. It was produced from molybdenum pentachloride , cyclopentadienyl sodium and sodium borohydride via molybdocene dihydride as an intermediate. The dihydride is converted to molybdocene dichloride when reacted with chloroform :
properties
In the molybdocene dichloride, the two cyclopentadienyl rings are angled to one another and not arranged coplanar as in the classic metallocenes . The average Cp-M-Cp angle is 130.6 °. The Cl-Mo-Cl angle is 82 °, which is less than the angle in zirconocene dichloride (92.1 °) and niobocene dichloride (85.6 °). This trend can be explained by the orientation of the HOMO in this class of compounds.
use
In contrast to the analogous zirconocene dichloride and titanocene dichloride , no technical application has been found for molybdocene dichloride. Like many other metallocene dichlorides, molybdocene dichloride is a potential active ingredient in cancer therapy, but so far it has not been able to show the expected results in clinical studies.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet bis (cyclopentadienyl) molybdenum (IV) dichloride from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on June 21, 2014 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c data sheet bis (cyclopentadienyl) molybdenum dichloride, 99% from AlfaAesar, accessed on June 21, 2014 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ RL Cooper, MLH Green: Some bis-π-cyclopentadienyl halides of molybdenum, tungsten, and rhenium . In: Journal of the Chemical Society A: Inorganic, Physical, Theoretical . 1967, p. 1155–1160 , doi : 10.1039 / J19670001155 .
- ↑ Ned D. Silavwe, Michael P. Castellani, David R. Tyler "Bis (η5-Cyclopentadienyl) Molybdenum (IV) Complexes" Inorganic Syntheses 1992, volume 29, p. 204-211. doi : 10.1002 / 9780470132609.ch50
- ↑ K. Prout, TS Cameron, RA Ford, SR Critchley, B. Denton, GV Rees: The crystal and molecular structures of bent bis-π-cyclopentadienyl-metal complexes: (a) bis-π-cyclopentadienyldibromorhenium (V) tetrafluoroborate, (b) bis-π-cyclopentadienyldichloromolybdenum (IV), (c) bis-π-cyclopentadienylhydroxomethylaminomolybdenum (IV) hexafluorophosphate, (d) bis-π-cyclopentadienylethylchloromolybdenum (IV), (e) bis-π-cyclopentoniadienyldichloro f) bis-π-cyclopentadienyldichloromolybdenum (V) tetrafluoroborate, (g) μ-oxo-bis [bis-π-cyclopentadienylchloroniobium (IV)] tetrafluoroborate, (h) bis-π-cyclopentadienyldichlorozirconium . In: Acta Cryst. B30, 1974, p. 2290-2304 , doi : 10.1107 / S0567740874007011 .
- ↑ Rosette M. Roat-Malone: Bioinorganic Chemistry. Wiley, 2007, ISBN 978-0-470-19170-5 , p. 20 ( limited preview in Google book search).
- ↑ Waern, JB, Dillon, CT, Harding, MM: Organometallic Anticancer Agents: Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity Studies on Thiol Derivatives of the Antitumor Agent Molybdocene Dichloride . In: J. Med. Chem. . 48, No. 6, 2005, pp. 2093-2099. doi : 10.1021 / jm049585o .

![{\ displaystyle \ mathrm {MoH_ {2} (C_ {5} H_ {5}) _ {2} + \ 2 \ CHCl_ {3} \ {\ xrightarrow [{}] {}} \ MoCl_ {2} (C_ {5} H_ {5}) _ {2} + \ 2 \ CH_ {2} Cl_ {2}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7603c4372f0e8cf4b69ad4a1980633b1ac04562d)