Molybdenum (V) chloride
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Molybdenum (V) chloride | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Molybdenum pentachloride |
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | MoCl 5 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
black solid with a pungent odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 273.21 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
2.928 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
194 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
268 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
2.33 hPa (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
decomposes in water with violent reaction |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Molybdenum (V) chloride is an inorganic chemical compound of molybdenum from the group of chlorides .
Extraction and presentation
Molybdenum (V) chloride can be obtained by reacting molybdenum in oxygen-free chlorine . Before the reaction, the metal powder should be heated to high temperatures in a stream of hydrogen or oxygen-free nitrogen to remove any surface oxide. It must then be ensured that before the actual reaction with chlorine, air and moisture are completely removed and kept away from the reaction.
It can also be obtained by reacting molybdenum (VI) oxide with carbon tetrachloride under pressure.
properties
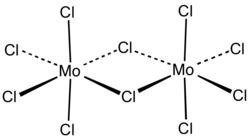
Molybdenum (V) chloride is a non-flammable, extremely hygroscopic , blue-black, paramagnetic solid with a pungent odor, which decomposes in water with violent reaction. If it has a dark green color, this is caused by the presence of oxide chlorides . The compound is soluble in water and alcohol (dark green solution) with solvolysis . It is soluble without decomposition in organic solvents such as ether , trichloromethane , carbon tetrachloride (dark red solution), carbon disulfide . Molybdenum (V) chloride has a monoclinic crystal structure with the space group C 2 / m (space group no. 12) , a = 1731 pm, b = 1781 pm, c = 607.9 pm, β = 95.7 °. It does not correspond to that of niobium (V) chloride . In addition to the α-form, three other modifications are also known. The β-form has a triclinic crystal structure with the space group P 1 (No. 2) , the γ-form an orthorhombic crystal structure with the space group Pnma (No. 62) and the δ-form a monoclinic crystal structure with the space group P 2 1 / c (No. 14) .
Molybdenum (V) chloride is in solid form as a dimer , whereas in the gaseous state it looks red and is present as a monomer .
use
Molybdenum (V) chloride is used to separate molybdenum.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Entry on molybdenum (V) chloride in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on August 24, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Data sheet Molybdenum (V) chloride, anhydrous at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on July 4, 2013 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Georg Brauer (Ed.) U. a .: Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 3rd, revised edition. Volume III, Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1981, ISBN 3-432-87823-0 , p. 1534.
- ^ AP Hagen: Inorganic Reactions and Methods, The Formation of Bonds to Halogens . John Wiley & Sons, 2009, ISBN 0-470-14539-0 , pp. 171 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ A b Mary Eagleson: Concise Encyclopedia Chemistry . Walter de Gruyter, 1994, ISBN 3-11-011451-8 , p. 662 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ J. Beck, F. Wolf: Three New Polymorphic Forms of Molybdenum Pentachloride. In: Acta Crystallographica Section B Structural Science. 53, 1997, pp. 895-903, doi : 10.1107 / S0108768197008331 .
- ^ Dale L. Perry: Handbook of Inorganic Compounds, Second Edition . Taylor & Francis US, 2011, ISBN 1-4398-1462-7 , pp. 281 ( limited preview in Google Book search).

