N -chlorosuccinimide
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
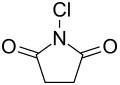
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | N -chlorosuccinimide | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 4 H 4 ClNO 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid with a smell of chlorine |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 133.53 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.65 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
148-151 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
216.5 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
14 g l −1 in water (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−357.9 kJ / mol |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
N -chlorosuccinimide , usually referred to as NCS for short, is the nitrogen- chlorinated imide of succinic acid .
Extraction and presentation
NCS can be made by treating succinimide with elemental chlorine .
properties
The heat of decomposition determined by DSC is −215 kJ · mol −1 or −1610 kJ · kg −1 .
use
On a laboratory scale, NCS is mainly used as a chlorinating agent, for example in the chlorination of alkenes in the allyl position or of alkyl aromatics in the benzyl position . It is used in larger quantities in the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients (especially antibiotics ). Compared to elemental chlorine (a caustic, poisonous gas), NCS is easier to store, handle and dose. When NCS is converted, the water-soluble succinimide is formed as a by-product .
The use of N -chlorosuccinimide as a chlorinating agent is an example of a synthesis method which proceeds with low atom economy .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet N-chlorosuccinimide (PDF) from Merck , accessed on February 28, 2010.
- ↑ a b Data sheet N-Chlorosuccinimide from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 12, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-25.
- ↑ Grewer, T .; Klais, O .: Exothermic decomposition - investigations of the characteristic material properties , VDI-Verlag, series "Humanisierung des Arbeitsleben", Volume 84, Düsseldorf 1988, ISBN 3-18-400855-X , p. 10.

