Neodymium (II) bromide
| Crystal structure | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||
| __ Nd 2+ __ Br - | |||||||
| General | |||||||
| Surname | Neodymium (II) bromide | ||||||
| other names |
Neodymium dibromide |
||||||
| Ratio formula | NdBr 2 | ||||||
| Brief description |
dark green solid |
||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||
|
|||||||
| properties | |||||||
| Molar mass | 304.05 g mol −1 | ||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||
| Melting point |
725 ° C |
||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||
|
|||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||
Neodymium (II) bromide is an inorganic chemical compound of neodymium from the group of bromides .
presentation
Neodymium (II) bromide can be obtained by reducing neodymium (III) bromide with neodymium in a vacuum at 800 to 900 ° C.
properties
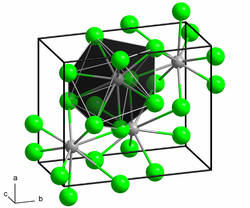
Neodymium (II) bromide is a dark green solid. The connection is extremely hygroscopic and can only be stored and handled under carefully dried protective gas or in a high vacuum. In air or in contact with water, it changes into hydrates when moisture is absorbed , but these are unstable and more or less quickly turn into oxide bromides with evolution of hydrogen . The compound has a crystal structure of lead (II) chloride type.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Georg Brauer (Ed.), With the collaboration of Marianne Baudler u. a .: Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 3rd, revised edition. Volume I, Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1975, ISBN 3-432-02328-6 , p. 1081.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
