Neophyl chloride
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Neophyl chloride | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 13 Cl | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
light yellow liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 168.66 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.047 g cm −3 (25 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
95-96 ° C (10 mmHg ) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
very soluble in acetone , benzene , diethyl ether and ethanol |
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.524 (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
Neophyl chloride is a chemical compound from the group of chlorinated hydrocarbons .
Extraction and presentation
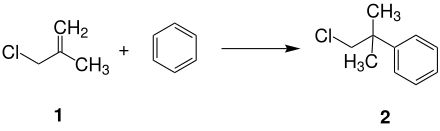
Neophyl chloride ( 2 ) can be obtained by alkylating benzene with 3-chloro-2-methylpropene ( 1 ) in the presence of sulfuric acid.
Neophyl chloride can also be prepared by chlorination of tert- butylbenzene (for example with sulfuryl chloride ).
properties
Neophyl chloride is a light yellow liquid that is very soluble in acetone , benzene , diethyl ether and ethanol .
use
Neophyl chloride is used as an intermediate for organic syntheses (for example fenbutatin oxide ).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h data sheet 2-chloromethyl-2-phenylpropane, 99% from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on January 9, 2019 ( PDF ).
- ^ A b William M. Haynes: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . CRC Press, 2016, ISBN 978-1-4987-5429-3 , pp. 104 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Harry H. Szmant, Szmant: Organic Building Blocks of the Chemical Industry . John Wiley & Sons, 1989, ISBN 0-471-85545-6 , pp. 346 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ WT Smith, Jr. and JT Sellas: Neophyl chloride In: Organic Syntheses . 32, 1952, p. 90, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.032.0090 ; Coll. Vol. 4, 1963, p. 702 ( PDF ).
- ^ William E. Truce, ET McBee, CC Alfieri: Chlorination of t-Butylbenzene to 1-Chloro-2-methyl-2-phenylpropane. In: Journal of the American Chemical Society. 71, 1949, p. 752, doi : 10.1021 / ja01170a520 .
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook . William Andrew, 1996, ISBN 978-0-8155-1853-2 , pp. 400 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ^ Frank C. Whitmore, Cyrus A. Weisgerber, AC Shabica: Formation of Cyclopropanes from Monohalides. IV. Some Reactions of 1-Chloro-2-methyl-2-phenylpropane (Neophyl Chloride). In: Journal of the American Chemical Society. 65, 1943, p. 1469, doi : 10.1021 / ja01248a010 .