Fenbutatin oxide
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
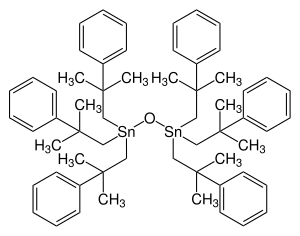
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Fenbutatin oxide | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 60 H 78 OSn 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 1052.70 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.31 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
145 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
230 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
0.49 µPa (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water (0.013 mg l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Fenbutatin oxide is a chemical compound from the group of organotin compounds .
Extraction and presentation
Fenbutatin oxide can be obtained by reacting neophyl chloride with magnesium , tin tetrachloride and sodium hydroxide solution .
properties
Fenbutatin oxide is a colorless solid that is practically insoluble in water. It decomposes when heated above 230 ° C. It is very stable under the influence of light, heat and oxygen and, depending on the temperature, converts to tris (2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl) tin hydroxide in water. In the soil it metabolizes to dihydroxy-bis (2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl) -stannate and 2-methyl-2-phenylpropylstannic acid. In soils, fenbutatin oxide shows a strong tendency to attach to cationic surfaces and organic components.
use
Fenbutatin oxide is used as an acaricide . It is a non-systemic acaricide with contact and feeding effects and is used against all agile stages of spider mites in fruit, vine and ornamental plant cultivation.
Admission
In the member states of the European Union, the active ingredient fenbutatin oxide was declared eligible for approval with effect from June 1, 2011 “for use as an acaricide in greenhouses”.
In Germany, Austria and Switzerland, no pesticides with this active ingredient are permitted. Preparations with fenbutatin oxide are approved in France, Italy, the Netherlands and Belgium, among others.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k Entry on bis (tris (2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl) tin) oxide in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 9, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d Müfit Bahadir, Harun Parlar, Michael Spiteller: Springer Umweltlexikon . Gabler Wissenschaftsverlage, 2000, ISBN 3-540-63561-0 , p. 425 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Entry on Bis (tris (2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl) tin) oxide in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook . William Andrew, 1996, ISBN 0-8155-1853-6 , pp. 400 (English, limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ^ Terence Robert Roberts, Terence Robert Roberts DH Hutson: Metabolic Pathways of Agrochemicals: Part 2: Insecticides and Fungicides . Royal Society of Chemistry, 1999, ISBN 0-85404-499-X , pp. 532 (English, limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Chemical and Veterinary Investigation Office Stuttgart: Use of the SFE - LC / MS for the determination of residues in food .
- ↑ Directive 2011/30 / EU of the Commission of March 7, 2011 amending Council Directive 91/414 / EEC to include the active substance fenbutatin oxide and amending Commission Decision 2008/934 / EC .
- ↑ a b Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Fenbutatin oxide in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on February 24, 2016.

