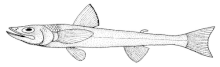
Reticulated eye fish
| Reticulated eye fish | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Bathypterois sp. |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Ipnopidae | ||||||||||||
| Gill , 1884 |
The net-eye fish (Ipnopidae) are deep-sea fish from the order of the lizard fish relatives (Aulopiformes). They live in the Atlantic , Indian and Pacific on the bottom of the deep sea .
features
Reticulated eye fish can grow to be 12 to 38 centimeters long. They are slim floor dwellers. Their scales are large and the lateral line organ is well developed. The lower jaw protrudes further than the upper jaw. The number of branchiostegal rays is 8 to 17, those of the vertebrae 44 to 80. Adult reticulated eye fish do not have an ocular gill gland (pseudobranch). Pyloric tubes are missing.
Fin formula : dorsal 8–16, anal 7–19, pectoral 9–24.
In the species of the first four genera listed below, the eyes are stunted or overgrown with skin. In the genus Ipnops , the eyes have no lenses. They are directed upwards.
The 19 species of tripod fish ( bathypterois ) have elongated fin rays on the pectoral and ventral fins and on the lower part of the caudal fin. They can stand on their pelvic and caudal fin rays like on a tripod on the sea floor and wait for prey .
Systematics
There are about 30 species in six genera and two subfamilies:
- Subfamily Ipnopinae
-
Bathymicrops
- Bathymicrops belyaninae Nielsen & Merrett, 1992 .
- Bathymicrops brevianalis Nielsen, 1966 .
- Bathymicrops multispinis Nielsen & Merrett, 1992 .
- Bathymicrops regis Hjort & Koefoed, 1912 .
-
Three leg fish ( Bathypterois )
- Bathypterois andriashevi Sulak & Shcherbachev, 1988 .
- Bathypterois atricolor Alcock , 1896 .
- Bathypterois bigelowi Mead, 1958 .
- Bathypterois Dubius Vaillant , 1888 .
- Bathypterois filiferus Gilchrist, 1906 .
- Bathypterois grallator ( Goode & Bean , 1886) .
- Bathypterois guentheri Alcock, 1889 .
- Bathypterois insularum Alcock, 1892 .
- Bathypterois longicauda Günther , 1878 .
- Bathypterois longifilis Günther, 1878 .
- Bathypterois longipes Günther, 1878 .
- Bathypterois oddi Sulak, 1977 .
- Bathypterois parini Shcherbachev & Sulak, 1988 .
- Bathypterois pectinatus Mead, 1959 .
- Bathypterois perceptor Sulak, 1977 .
- Bathypterois phenax Parr, 1928 .
- Bathypterois quadrifilis Günther, 1878 .
- Bathypterois ventralis Garman , 1899 .
- Bathypterois viridensis (Roule, 1916) .
-
Bathytyphlops
- Bathytyphlops marionae Mead, 1958 .
- Bathytyphlops sewelli (Norman, 1939) .
-
Ipnops
- Ipnops agassizii Garman, 1899 .
- Ipnops meadi Nielsen, 1966 .
- Ipnops murrayi Günther, 1878 .
-
Bathymicrops
- Subfamily Bathysauropsinae
-
Bathysauropsis Regan, 1911 .
- Bathysauropsis gracilis (Günther, 1878)
- Bathysauropsis malayanus (Fowler, 1938)
-
Bathysauropsis Regan, 1911 .
literature
- Joseph S. Nelson, Terry C. Grande, Mark VH Wilson: Fishes of the World. Wiley, Hoboken, New Jersey, 2016, ISBN 978-1118342336
- Kurt Fiedler: Textbook of Special Zoology, Volume II, Part 2: Fish . Gustav Fischer Verlag Jena, 1991, ISBN 3-334-00339-6
Web links
- Ipnopidae on Fishbase.org (English)