Nitrosamines
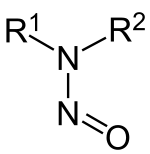
Nitrosamines , more precisely N -nitrosamines, are a class of organic-chemical compounds that are derived from secondary amines . They have the general structural formula R 1 R 2 N-NO; R 1 and R 2 are alkyl or aryl radicals. Nitrosamines are carcinogenic and are of no industrial importance.
properties
Under standard conditions , nitrosamines are mostly liquid or solid. Because of the hydrophilic N − N = O grouping, they are soluble in water and other polar solvents. The density varies between 0.9 and 1.2 g per cm³ .
If R 1 and R 2 are organyl radicals , the nitrosamines are more stable than if R 1 or R 2 stands for a hydrogen atom.
Emergence
Nitrosamines arise from secondary amines through the action of nitrosating agents (nitrous acid and its salts the nitrites , nitrogen oxides ). Nitrosamines are formed in an acidic environment, as is also the case endogenously in the human stomach . HNO 2 is initially formed from nitrite . After renewed protonation, this splits into a nitrosyl cation (NO + ) and water [see (1)]. The nitrosyl cation reacts with the amine to form nitrosamine [see (2)]. On the other hand, nitrosamines can also be produced endogenously by the body's own bacteria.
- (1)
- (2)
In the atmosphere, nitrosamines are also formed photochemically from suitable amines through the action of nitrogen oxides. Incomplete combustion of nitrogen-rich materials can also lead to the formation of nitrosamines.
Occurrence
There are no indications of the presence of nitrosamines in foods of plant origin, in soils or in groundwater. They occur - typically in very small doses - in many foods , for example in beer , fish , cured meat products or in cheese . N -nitrosamines are reaction products of nitrite and secondary amines (as in proteins ), which are mainly formed when exposed to heat. When heating cured foods and reheating spinach , the intracellular nitrate deposits of which have been microbially converted to nitrite, there is also the risk of nitrosamine formation.
Nitrosamines can also be found in latex mattresses , balloons , condoms and tobacco . The ALARA principle applies to children's toys made of natural and synthetic rubber that are put in the mouth . Manufacturers can largely avoid the formation of carcinogenic N -nitrosamines by selecting suitable vulcanization accelerators.
A momentous example of the undesirable occurrence of nitrosamines can be seen at the old Continental AG headquarters in Hanover-Limmer. Today there are still two sections of an old building complex under monument protection, which had to be abandoned at the time due to walls contaminated with nitrosamines and have not yet been renovated. It was also not possible to use the old company premises until recently. Only after extensive renovation and excavation of the soil can new living space be created there. The two parts of the building contaminated with nitrosamines are still under monument protection, but entering the area is prohibited for health reasons.
Nitrosamines can also arise in cooling lubricants mixed with water - from nitrate converted into nitrite from the water used and amines that have been carried over (leftover food, cigarettes). The key component is N -nitroso-diethanolamine (NDELA), (HOC 2 H 4 ) 2 N – NO.
Health effects
In animal experiments , 90% of the nitrosamines examined were found to have a strong carcinogenic effect in all species. Nitrosamines are precarcinogens, which means that they have to be activated in the body so that they can develop their harmful effects. This takes place through a cytochrome P450 -catalyzed reaction. In subsequent reactions, the very reactive formaldehyde and carbonium ions are released, which have a strong genotoxic effect.
Epidemiological studies indicate a positive correlation between nitrite and nitrosamine intake and gastric cancer , as well as between the consumption of meat and sausage products and gastric and esophageal cancer .
Further epidemiological studies also see a correlation between the increasing use of nitrate and nitrite in agriculture (fertilization) and the food industry (preservatives), the resulting increased exposure to nitrosamines and the increasing number of Alzheimer's , Parkinson's and diabetes cases .
In animal experiments, nitrosamines have also caused damage to the liver and genetic material .
Nitrosodialkylamines (R 1 , R 2 = alkyl radical ) are metabolized in the body to alkyl diazohydroxides, which are the ultimate carcinogens, i.e. they actually have a carcinogenic effect. With the release of nitrogen, these disintegrate into highly reactive carbenium ions, which can form adducts with DNA, RNA and proteins. N -nitrosodimethylamine, for example, methylates the DNA bases guanine and adenine.
proof
Nitrosamines are detected, among other things, by a chemiluminescence detector or by high-resolution mass spectrometry, each after separation by gas chromatography .
literature
- Ahmed Askar: Amines and Nitrosamines - Occurrence, Significance, Metabolism and Purpose. 2nd unchanged edition. Technical University of Berlin, Institute for Food Technology, Berlin 1979, ISBN 3-7983-0204-9 .
- G. Eisenbrand, M. Metzler: Toxicology for Chemists. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart 1994, ISBN 3-13-127001-2 , p. 66.
proof
- ↑ a b c Entry on nitrosamines. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 12, 2014.
- ↑ Toys made of natural and synthetic rubber for children under three years of age: The release of N-nitrosamines should be as low as possible , BfR opinion No. 005/2012 of January 17, 2011.
- ↑ https://wasserstadt.haz.de/2019/12/10/papenburg-darf-conti-gebaeude-auf-wasserstadtareal-nicht-abreissen/
- ↑ Sharma Veena, Singh Rashmi: A Review on Mechanism of Nitrosamine Formation, Metabolism and Toxicity in In Vivo. (No longer available online.) Archived from the original on December 25, 2016 ; accessed on December 24, 2016 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ P. Jakszyn, CA Gonzalez: Nitrosamine and related food intake and gastric and oesophageal cancer risk: a systematic review of the epidemiological evidence. World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Jul 21; 12 (27), pp. 4296-4303, PMID 16865769 .
- ↑ Suzanne M. De la Monte, Alexander Neusner, Jennifer Chu, Margot Lawton: Epidemilogical Trends Strongly Suggest Exposures as Etiologic Agents in the Pathogenesis of Sporadic Alzheimer's Disease, Diabetes Mellitus, and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. In: Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. 17: 3 (July 2009), pp. 519-529, PMID 19363256 .
- ↑ Sodium nitrite (zuatzstoffe-online.de).