Ohira-Bestmann reagent
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Ohira-Bestmann reagent | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 5 H 9 N 2 O 4 P | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
yellowish or reddish liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 192.11 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.268–1.282 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.477-1.482 (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
Ohira-Bestmann reagent is a chemical compound from the ester group . It was developed in the 1990s by Susumu Ohira and Hans Jürgen Bestmann for a modified Seyferth-Gilbert reaction .
Extraction and presentation
The Ohira-Bestmann reagent can be obtained, for example, by reacting dimethyl 2-oxopropylphosphonate with sodium hydride and then reacting it with a sulfonyl azide .
properties
The Ohira-Bestmann reagent is a yellowish or reddish liquid.
use
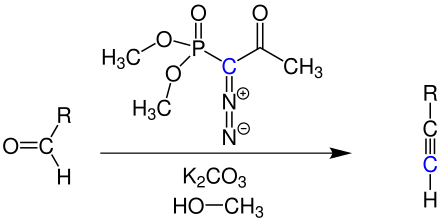
The Ohira-Bestmann reagent is used as an effective reagent for the one-step conversion of aldehydes to alkynes compared to the multi-step Corey-Fuchs method .
The generation of dimethyl (diazomethyl) phosphonate in situ through the reaction of Ohira-Bestmann reagent with methanol and potassium carbonate ensures a high yield in the synthesis of terminal alkynes. R corresponds to an organic residue.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Zerong Wang: Comprehensive organic name reactions and reagents . John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ 2009, ISBN 978-0-471-70450-8 , pp. 2559-2560 .
- ↑ a b c d Entry on Dimethyl (1-Diazo-2-oxopropyl) phosphonate at TCI Europe, accessed on November 3, 2019.
- ↑ a b c d Data sheet Dimethyl (1-diazo-2-oxopropyl) phosphonate solution, ~ 10% in acetonitrile (H-NMR), ≥96% (HPLC) from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on November 3, 2019 ( PDF ) .
- ^ S. Müller, B. Liepold, GJ Roth, HJ Bestmann: An Improved One-pot Procedure for the Synthesis of Alkynes from Aldehydes . In: Synlett . tape 6 , 1996, pp. 521-522 , doi : 10.1055 / s-1996-5474 .
- ↑ Methanolysis of Dimethyl (1-Diazo-2-oxopropyl) Phosphonate: Generation of Dimethyl (Diazomethyl) Phosphonate and Reaction with Carbonyl Compounds . In: Synthetic Communications: An International Journal for Rapid Communication of Synthetic Organic Chemistry . tape 19 , no. 3-4 , 1989, pp. 561-564 , doi : 10.1080 / 00397918908050700 .
- ↑ Jörg Pietruszka, Andreas Witt: Synthesis of the Bestmann-Ohira Reagent. In: Synthesis. 2006, 2006, p. 4266, doi : 10.1055 / s-2006-950307 .
- ↑ Tue Heesgaard Jepsen, Jesper Langgaard Kristensen: Generation of the Ohira-Bestmann Reagent from Stable Sulfonyl Azide: Scalable Synthesis of Alkynes from Aldehydes. In: The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 79, 2014, p. 9423, doi : 10.1021 / jo501803f .
- ^ Paul Knochel, Gary A Molander: Comprehensive Organic Synthesis . Newnes, 2014, ISBN 978-0-08-097743-0 , pp. 583 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ László Kürti, Barbara Czakó: Strategic applications of named reactions in organic synthesis: background and detailed mechanisms . Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam / Boston 2005, ISBN 0-12-429785-4 , pp. 402-403 .
- ^ GJ Roth, B. Liepold, SG Müller, HJ Bestmann: Further Improvements of the Synthesis of Alkynes from Aldehydes . In: Synthesis . tape 1 , 2004, p. 59-62 , doi : 10.1055 / s-2003-44346 .