Tetraethyl orthocarbonate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Tetraethyl orthocarbonate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 9 H 20 O 4 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
clear, colorless liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 192.25 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.91 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
158-159 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.3932 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Orthocarbonic acid tetraethyl ester is an orthocarbonic acid ester which is formally formed by complete ethylation of the orthocarbonic acid C (OH) 4 , which is unstable in the free state . Tetraethyl orthocarbonate C (OC 2 H 5 ) 4 was first described in 1864.
Extraction and presentation
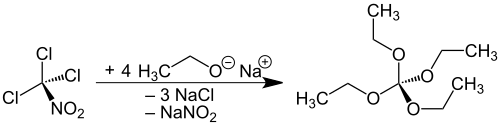
The representation of the orthocarbonic acid tetraethyl ester from the highly toxic chloropicrin used as a chemical warfare agent in the First World War is known from the literature. and only achieves yields of 46-49% to 58% of theory
As with the homologous tetramethyl orthocarbonate, the obvious synthetic route from carbon tetrachloride does not deliver the desired product.
Starting from trichloroacetonitrile , which is less toxic than chloropicrine, significantly higher yields (up to 85% of theory) can be achieved, as is the case with tetraethyl orthocarbonate. An alternative that circumvents problematic reactants is the reaction of dialkyltin dialkoxides with carbon disulfide at an elevated temperature in the autoclave:
A more recent synthesis starts directly from sodium ethoxide , tin (IV) chloride and carbon disulfide.
properties
Orthocarbonic acid tetraethyl ester is a water-clear, aromatic or fruity-smelling liquid that is incompatible with strong acids and strong bases.
use
Tetraethyl orthocarbonate can be used as a solvent and for the alkylation of CH-acidic compounds, e.g. B. phenols and carboxylic acids can be used. It also reacts with amines, enol ethers, sulfonamides and the like. Ä., Spiro compounds can also be obtained. Spiro-orthocarbonates (SOCs), which are used as additives to reduce shrinkage in the polymerization of epoxides, are of certain industrial interest .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Datasheet tetraethyl carbonate for synthesis (PDF) from Merck , accessed on October 17, 2013.
- ↑ a b H. Bassett, Ueber das quadruple basic kohlensaure Aethyl , Ann. 132, 54 (1864), doi : 10.1002 / jlac.18641320106 .
- ↑ H. Tieckelmann, HW Post, The preparation of methyl, ethyl, propyl, and butyl orthocarbonates , J. Org. Chem., 13 (2), 265-267 (1948), doi : 10.1021 / jo01160a014 .
- ↑ a b J.D. Roberts, RE McMahon: Ethyl Orthocarbonate In: Organic Syntheses . 32, 1952, p. 68, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.032.0068 ; Coll. Vol. 4, 1963, p. 457 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b European patent specification EP 0881212 B1, Production method of aminobenzene compound , inventor: H. Hashimoto et al., Applicant: Takeda Chemical Industries, Ltd., published October 30, 2001.
- ^ RH De Wolfe, Carboxylic ortho acid derivatives: Preparation and synthetic applications , Organic Chemistry, Vol. 14, Academic Press, Inc. New York - London, 1970, ISBN 978-0-12-214550-6 .
- ↑ US patent US 6825385, Process for the preparation of orthocarbonates , inventor: G. Fries, J. Kirchhoff, applicant: Degussa AG, issued November 30, 2004.
- ↑ S. Sakai et al., Reaction of Dialkyltin Dialkoxides with Carbon Disulfide at Higher Temperature. Preparation of Orthocarbonates , J. Org. Chem., 36 (9), 1176 (1971), doi : 10.1021 / jo00808a002 .
- ↑ S. Sakai et al., A new method for preparation of tetraalkyl orthocarbonates from sodium alkoxides, tetrachlorostannane, and carbon disulfide, Synthesis 1984 (3), 233-234, doi : 10.1055 / s-1984-30785 .
- ^ JH Ruth, Odor Thresholds and Irritation Levels of Several Chemical Substances: A Review , Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 47, A-142 - A-151, (1986).
- ↑ Data sheet orthocarbonic acid tetraethyl ester from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on October 17, 2013 ( PDF ).
- ↑ W. Kantlehner et al., The preparative chemistry of the O- and N-functional orthocarbonic acid derivatives , Synthesis, 1977, 73-90.
- ↑ DT Vodak et al., One-Step Synthesis and Structure of an Oligo (spiro-orthocarbonate) , J. Am. Chem., Soc., 124 , 4942-4943 (2002), doi : 10.1021 / ja17683i .
- ↑ R. Acosta Ortiz et al., Novel diol spiro orthocarbonates derived from glycerol as anti-shrinkage additives for the cationic photopolymerization of epoxy monomers , Polymer International, 59 (5), 680-685 (2010), doi : 10.1002 / pi. 2755 .