Tetramethyl orthocarbonate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Tetramethyl orthocarbonate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 5 H 12 O 4 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 136.15 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.023 g cm −3 (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−5.5 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
114 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in salt solution, miscible with methanol and dioxane |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.3864 (18.5 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Tetramethyl orthocarbonate is an organic chemical compound from the group of orthocarbonic acid esters . Formally, it arises through complete methylation of the hypothetical, i.e. H. Orthocarbonic acid which violates the Erlenmeyer rule and is unstable in the free state . Tetramethyl orthocarbonate was first presented in 1927 and characterized as a colorless, noticeably volatile liquid with a camphor-like odor.
Extraction and presentation
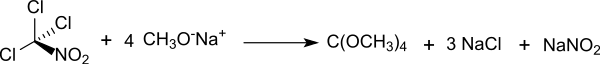
The original preparation of the orthocarbonic acid tetramethyl ester was based on chloropicrin , the obvious synthetic route from carbon tetrachloride does not deliver the desired product.
Because of the unfavorable characteristics of the other chloropicrin tetrasubstituted methane reactive derivatives have been investigated as raw materials for Orthokohlensäuretetramethylester so employed also as a chemical warfare agent, from simple carbon disulphide and chlorine accessible trichloromethanesulfenyl analog
A less problematic synthetic route starts from trichloroacetonitrile , yields of around 70% being achieved.
Further preparative processes for the preparation of orthocarboxylic acid esters are described.
properties
Tetramethyl orthocarbonate is a water-clear, aromatic-smelling, low-viscosity liquid that is stable against the formation of peroxides.
use
In addition to being used as a solvent, tetramethyl orthocarbonate is used as a fuel in solid polymer fuel cells , as an alkylating agent at elevated temperatures (180-200 ° C), as a transesterification reagent , but which is less reactive than trimethyl orthoformate and as a reagent for the synthesis of 2-aminobenzoxazoles, which are used as molecular building blocks in pharmaceutical active ingredients, e.g. B. neuroleptics , sedatives , antiemetics , muscle relaxants , fungicides , u. a. can be found.
Depending on the substituents, the one-pot reaction proceeds in “modest to excellent” yields.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g H. v. Hartel, On the existence and representation of the orthocarbonic acid tetramethyl ester , Ber.dtsch.chem.Ges., 60 (8), 1841 (1927), doi : 10.1002 / cber.19270600821 .
- ↑ a b c d data sheet of tetramethyl orthocarbonate from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on October 16, 2013 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b R. H. De Wolfe, Carboxylic ortho acid derivatives: preparation and synthetic applications , Organic Chemistry, Vol. 14, Academic Press, Inc. New York - London, 1970, ISBN 978-0-12-214550-6 .
- ↑ H. Tieckelmann, HW Post, The preparation of methyl, ethyl, propyl, and butyl orthocarbonates , J. Org. Chem., 13 (2), 265-267 (1948), doi : 10.1021 / jo01160a014 .
- ↑ US Patent US 4,059,656, Processes for neutralizing 2,3-dibromopropanol phosphoric acid esters contained in tris (2,3-dibromo-1-propyl) phosphate , inventor: M. Demarcq, applicant: Produits Chimiques Ugine Kuhlmann, issued on 22 November 1974.
- ↑ US Patent US 3,876,708, Orthocarbonic acid esters , inventors: R. Speh, W. Kantlehner, applicant: Akzo BV, issued April 8, 1975.
- ↑ US patent US 6,825,385 B2, Process for the preparation of orthocarbonates , inventor: G. Fries, J. Kirchhoff, applicant: Degussa AG, issued November 30, 2004.
- ↑ W. Kantlehner et al., The preparative chemistry of the O- and N-functional orthocarbonic acid derivatives , Synthesis ; 1977 (2): 73-90, doi : 10.1055 / s-1977-24283 .
- ^ KR Kopecky, J. Molina: Bis (dimethoxymethyl) peroxide and bis (1,1-dimethoxyethyl) peroxide . In: Canadian Journal of Chemistry . 65, 1987, p. 2350, doi : 10.1139 / v87-392 .
- ↑ US patent US 6,864,001, tetramethyl orthocarbonate fuel cells and systems and methods related , inventor: J. Zhang, K. Colbow, applicant: Ballard Power Systems Inc., issued on March 8, 2005.
- ↑ M. Selva et al., Esters and Orthoesters as Alkylating Agents at High Temperature. Applications to Continuous-Flow Processes , J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2, 519 (1992), doi : 10.1039 / P29920000519 .
- ↑ CL Cioffi et al., Synthesis of 2-Aminobenzoxazoles Using Tetramethyl Orthocarbonate or 1,1-Dichloro-diphenoxymethane , J. Org. Chem., 75 (2), 7942-7945 (2010), doi : 10.1021 / jo1017052 .