Osmium (IV) chloride
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
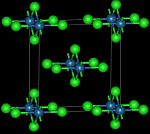
| High temperature mold | ||||||||||||||||
| Crystal system |
cubic |
|||||||||||||||
| Space group |
P 4 3 32 (No. 212) or P 4 1 32 (No. 213) (both room temperature modification) |
|||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Osmium (IV) chloride | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Osmium tetrachloride |
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | OsCl 4 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
red solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 332.012 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
|
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
450 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Osmium (IV) chloride is an inorganic chemical compound of osmium from the group of chlorides . It was first synthesized in 1909.
Extraction and presentation
Osmium (IV) chloride can also be prepared by disproportionation of osmium (III) chloride at 500 ° C in a vacuum .
Representation by reflux of thionyl chloride with osmium (VIII) oxide is also possible .
The black high-temperature form can be obtained by reacting osmium (VIII) oxide with carbon tetrachloride or osmium with thionyl chloride at 460 ° C.
The high-temperature form can also be obtained by reacting osmium with chlorine at around 700 ° C.
properties
Osmium (IV) chloride is a red to brown paramagnetic solid. It dissolves in water, hydrochloric acid and ethanol with a yellow color, but quickly decomposes in solution. The crystal structure consists of edge-sharing [OsCl 2 ] Cl 4/2 octahedra in a linear arrangement. There is also a black high-temperature form that sublimes in chlorine or vacuum to yellow vapors that arise depending on the synthesis method. At temperatures above 400 ° C, it forms osmium oxide tetrachloride OsOCl 4 with oxygen . The high-temperature form has an orthorhombic crystal structure with the space group Cmmm (space group no.65 ) , while the normal temperature form has a cubic crystal structure with the space group P 4 3 32 (space group no.212 ) or space group P 4 1 32 (space group no.213 ) owns.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f data sheet OSMIUM TETRACHLORIDE, Aldrich bei Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on January 31, 2016 ( PDF ).
- ^ Carl L. Yaws: The Yaws Handbook of Physical Properties for Hydrocarbons and Chemicals Physical Properties for More Than 54,000 Organic and Inorganic Chemical Compounds, Coverage for C1 to C100 Organics and Ac to Zr Inorganics . Gulf Professional Publishing, 2015, ISBN 978-0-12-801146-1 , pp. 740 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b F. Albert. Cotton, Catherine E. Rice: Structure of the high-temperature form of osmium (IV) chloride. In: Inorganic Chemistry. 16, 1977, p. 1865, doi : 10.1021 / ic50174a008 .
- ↑ a b Otto Ruff, Ferd. Bornemann: about osmium, its analytical determination, its oxides and its chlorides. In: Journal of Inorganic Chemistry. 65, 1910, p. 429, doi : 10.1002 / zaac.19100650126 .
- ↑ G. Singh: Chemistry Of Lanthanides And Actinides . Discovery Publishing House, 2007, ISBN 81-8356-241-8 , pp. 307 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b c d e Jane E. Macintyre: Dictionary of Inorganic Compounds . CRC Press, 1992, ISBN 978-0-412-30120-9 , pp. 2963 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ George Fownes: A Manual of Elementary Chemistry, Theoretical and Practical . HC Lea, 1873, p. 388 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Christoph Janiak, Hans-Jürgen Meyer, Dietrich Gudat, Ralf Alsfasser: Riedel Modern Inorganic Chemistry . Walter de Gruyter, 2012, ISBN 978-3-11-024901-9 , p. 356 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ Georg Bauer, Konrad Ruthardt: Elements of the eighth subgroup platinum metals platinum · palladium · rhodium · iridium ruthenium · osmium . Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-662-28796-5 , pp. 157 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b Paul Machmer: On the polymorphism of osmium tetrachloride. In: Chemical Communications (London). 1967, p. 610a, doi : 10.1039 / C1967000610A .




