Osmium (V) fluoride
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||
| __ F - | ||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | Osmium (V) fluoride | |||||||||
| other names |
Osmium pentafluoride |
|||||||||
| Ratio formula | OsF 5 | |||||||||
| Brief description |
blue-green solid |
|||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 285.22 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||
| Melting point |
70 ° C |
|||||||||
| boiling point |
225 ° C |
|||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
Osmium (V) fluoride is an inorganic chemical compound of osmium from the group of fluorides .
Extraction and presentation
Osmium (V) fluoride can be obtained by reacting osmium (VI) fluoride with iodine in iodine pentafluoride at 50 ° C or by decomposing osmium (VI) fluoride under UV light.
properties
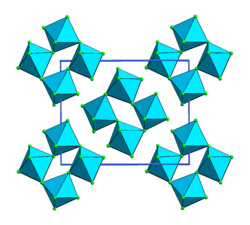
Osmium (V) fluoride is a blue-green, monoclinic solid. It melts at 70 ° C to a green liquid that turns blue when heated further. The connection is tetrameric in the form of corner-linked octahedra .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Georg Brauer (ed.), With the collaboration of Marianne Baudler a . a .: Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 3rd, revised edition. Volume I, Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1975, ISBN 3-432-02328-6 , p. 283.
- ↑ a b c d G. Singh: Chemistry Of Lanthanides And Actinides . Discovery Publishing House, 2007, ISBN 81-8356-241-8 , pp. 307 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Ralf Alsfasser, Erwin Riedel , HJ Meyer: Moderne Anorganische Chemie . Walter de Gruyter, 2007, ISBN 3-11-019060-5 , p. 343 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
