Oxazine
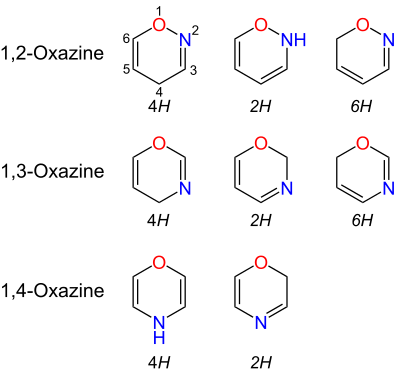
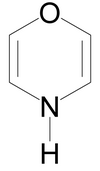
Oxazines (according to the Hantzsch-Widman system ) are heterocyclic , unsaturated carbon compounds that have both an oxygen and a nitrogen atom in the same six-membered ring system . Depending on the position of the heteroatoms, the corresponding substance is referred to as 1,2-oxazine, 1,3-oxazine or 1,4-oxazine. One of the simplest hydrogenated oxazines is morpholine ( tetrahydro-1,4-oxazine or 1,4-oxazinane ).
Occurrence
Oxazines occur very frequently in nature as dyes, such as litmus as indicator dye , and glycosides . The toxic oxazinines are very complex representatives .
properties
The presence of the two heteroatoms oxygen and nitrogen makes the oxazines ampholytes , i. that is, they have both acidic and basic properties. Furthermore, the polar substances are usually readily soluble in water. Aromatic oxazines very often show fluorescence .
use
Oxazines are used in the chemical-pharmaceutical industry as important starting / intermediate substances for drugs (e.g. antibiotics ) and as colorants (e.g. for CDs / DVDs).
Individual evidence
- ^ Theophil Eicher, Siegfried Hauptmann, Andreas Speicher: The Chemistry of Heterocycles: Structures, Reactions, Synthesis, and Applications , 3rd, Completely Revised and Enlarged Edition, John Wiley & Sons, p. 442 ( limited preview in the Google book search).