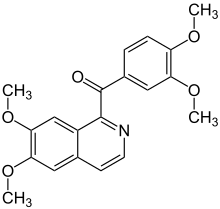
Papaveraldin
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Papaveraldin | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 20 H 19 NO 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 353.37 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
210 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Papaveraldin , also known as xanthaline , is a chemical substance with a benzylisoquinoline backbone. It belongs to the group of opium alkaloids .
Occurrence
With 0.5 to 3% (⌀ 1%) content papaveraldin is in addition to morphine (9 to 18%, ⌀ 10.5%), noscapine (previously also narcotine , 2 to 12%, ⌀ 5%), codeine (0, 2 to 6%, ⌀ 1%), papaverine (0.1–0.4%) as well as narceine (0.1 to 1%, ⌀ 0.5%), thebaine (0.2 to 1%, ⌀ 0, 5%) and laudanosine one of the main components of raw opium.
Synthesis and chemistry
Papaveraldin is an oxidation product of papaverine. The N -methylated derivative N-methylxanthalinium occurs naturally as a quaternary ammonium compound in the moon seed family ( Menispermaceae ) Stephania sasakii .
proof
The detection of papaveraldine can be done by high performance liquid chromatography . The analytes are separated with a water - methanol - acetonitrile mixture containing sodium lauryl sulphate via a reversed phase C-18 separation column .
Individual evidence
- ^ A b J. Buckingham: Dictionary of natural products. P. 4440, 1996, CRC Press, ISBN 0-412-46620-1 .
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ W. Blaschek, HHJ Hager, F. v. Bruchhausen, H. Hager: Hager's Handbook of Pharmaceutical Practice: Volume 2: Drugs AK. S. 296ff, 1998, Springer-Verlag, ISBN 3-540-61619-5 .
- ↑ Girreser, U., Hermann, TW and Piotrowska, K .: Oxidation and degradation products of papaverine. Part II [1]: investigations on the photochemical degradation of papaverine solutions. in: Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2003 Sep; 336 (9): 401-5 , PMID 14528487 .
- ↑ Colautti, A., Fontani, F. and Maurich, V .: HPLC determination of papaveraldine and papaverinol in papaverine injection. In: J Pharm Biomed Anal . 1987; 5: 493-499, PMID 16867493 .
