Pigment red 170
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Pigment red 170 | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 26 H 22 N 4 O 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
red odorless powder |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 454.48 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.4 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
315-325 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Pigment Red 170 is a chemical compound from the group of azo pigments .
Extraction and presentation
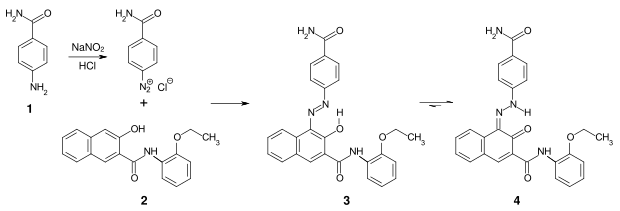
Pigment Red 170 ( 3 ) is industrially synthesized by the diazotization of p -aminobenzamide ( 1 ) and subsequent coupling with 3-hydroxy-2-naphtholic acid-2-ethoxyanilide ( 2 ), a naphthol AS derivative. In the solid state, these azo pigments are in the hydrazo form ( 4 ) ( azo-hydrazo-tautomerism ).
properties
Pigment Red 170 is a red, odorless and practically insoluble in water solid. The connection occurs in two crystal structures that differ in color cast and transparency. The phases have a monoclinic crystal structure with space group P 2 1 / c (space group no. 14) or space group P 2 1 / n (space group no. 14, position 2) .
use
Pigment Red 170 is used as a pigment for paints, varnishes and plastics ( e.g. PVC ). The compound was developed in the 1960s.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Werner Baumann, Thomas Rothardt: Printing chemicals data and facts on environmental protection 2nd, expanded and revised edition . Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-642-58474-9 , pp. 584 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ There is not yet a harmonized classification for this substance . A labeling of 4 - [(4-carbamoylphenyl) diazenyl] -N- (2-ethoxyphenyl) -3-hydroxy-2-naphthamide in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is shown, which is derived from a self-classification by the distributor on March 05, 2019.
- ↑ Registration dossier on 4 - [(4-carbamoylphenyl) diazenyl] -N- (2-ethoxyphenyl) -3-hydroxy-2-naphthamide ( GHS section ) at the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on March 5, 2019.
- ↑ a b Martin U. Schmidt, Detlef WM Hofmann u. a .: Crystal Structures of Pigment Red 170 and Derivatives, as Determined by X-ray Powder Diffraction. In: Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 45, 2006, p. 1313, doi : 10.1002 / anie.200502468 .
- ↑ a b Günter Etzrodt, Albrecht Müller: Plastics coloring colorants, fillers, regulations . Carl Hanser Verlag GmbH Co KG, 2018, ISBN 978-3-446-45714-0 , p. 114 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Warshamanage, Rangana & Linden, Anthony & U Schmidt, Martin & Buergi, hans-beat. (2014). Average structures of the disordered β-phase of Pigment Red 170: A single-crystal X-ray diffraction study. In: Acta crystallographica Section B, Structural science, crystal engineering and materials. 70, 283-95. doi : 10.1107 / S2052520614000407 .
- ↑ a b Willy Herbst, Klaus Hunger: Industrial organic pigments production, properties, application . John Wiley & Sons, 2009, ISBN 3-527-62496-1 , pp. 66 ( limited preview in Google Book search).