Plumban
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
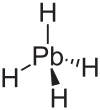
|
||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | Plumban | |||||||||
| other names |
Hydrogen lead |
|||||||||
| Molecular formula | PbH 4 | |||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 211.23 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| Physical state |
gaseous |
|||||||||
| boiling point |
−13 ° C |
|||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
Plumban , also known as hydrogen lead , is a very poisonous gas. It has the formula PbH 4 and has a boiling point of −13 ° C.
Extraction and presentation
Plumban is created by the action of atomic hydrogen on finely divided lead . It is also formed when Dimethylplumban having the formula (CH 3 ) 2 PbH 2 above -50 ° C disproportionated . Plumban is produced in small quantities as a by-product in the manufacture of tetraethyl lead.
properties
In contrast to methane (CH 4 ), which has an analogous structure , plumban is chemically unstable. When the gas is passed over a heated surface, it breaks down and a lead mirror is deposited. The reason for this is that lead, as a metal, is more electropositive than the bound hydrogen atoms, i.e. it binds the hydrogen as a hydride.
Derivatives with organic substituents, for example, are more stable than plumban
- Tetramethyl lead Pb (CH 3 ) 4 or
- Tetraethyl lead Pb (C 2 H 5 ) 4 (TEL).
These substances were used as anti - knock agents before the development of lead-free petrol . Since they can be absorbed by the skin and are toxic (MAK value of TEL 0.075 mg / m 3 ), gasoline containing lead has been banned in Germany since 1998 and throughout the European Union since 2000.
Individual evidence
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 , p. 1011.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.