Polyacrylamide
| Structural formula | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
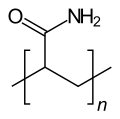
|
|||||||
| General | |||||||
| Surname | Polyacrylamide | ||||||
| other names |
Poly (2-propenamide) |
||||||
| CAS number | 9003-05-8 | ||||||
| Monomer | Acrylamide | ||||||
| Molecular formula of the repeating unit | C 3 H 5 NO | ||||||
| Molar mass of the repeating unit | 71.08 g mol −1 | ||||||
| properties | |||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||
| density |
0.75–0.95 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||
|
|||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||
Polyacrylamide (PAM) is a polymer of acrylamide .
Polyacrylamide can be produced from acrylamide in an aqueous solution by radical polymerisation . The reaction can e.g. B. ammonium persulfate (APS) initiated as a radical starter and catalyzed by tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED) .
Polyacrylamide is water-soluble or at least it is swollen by water. Dilute aqueous solutions of polyacrylamides with low molar masses have a higher viscosity than pure water. When adding small amounts of polyacrylamide with a high molar mass to water, a gel is formed with a consistency that is roughly the same as that of jelly .
In the unpolymerized form, acrylamide is a neurotoxin , in the polymerized form it is harmless.
application
- Polyacrylamide is used as a gel in polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis .
- It is used as a gel former in the cosmetics industry.
- It is used as an aid in oil production (tertiary oil production, polymer flooding).
- Copolymers with cationic esterquats are used as retention aids in paper manufacture and as flocculants in wastewater engineering .
- Copolymers with acrylic acid , especially when they are crosslinked with polyvalent acrylates, are used as superabsorbents, for example in diapers .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Polyacrylamide data sheet (PDF) from Carl Roth , accessed on April 9, 2010.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ Arnold Willmes, Pocket Book Chemical Substances , Harri Deutsch, Frankfurt (M.), 2007.