Protactinium (IV) oxide
| Crystal structure | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||
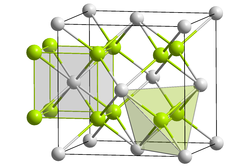
| __ Pa 4+ __ O 2− | |||||||
| Crystal system | |||||||
| Space group |
Fm 3 m (No. 225) |
||||||
| Lattice parameters |
a = 550.5 pm |
||||||
| Coordination numbers |
Pa [8], O [4] |
||||||
| General | |||||||
| Surname | Protactinium (IV) oxide | ||||||
| Ratio formula | PaO 2 | ||||||
| Brief description |
black solid |
||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||
|
|||||||
| properties | |||||||
| Molar mass | 263.04 g mol −1 | ||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||
| Hazard and safety information | |||||||
 Radioactive |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||
Protactinium (IV) oxide is a chemical compound of protactinium and oxygen with the formula PaO 2 . It's a black, crystalline powder. It has a cubic crystal system , the space group Fm 3 m (space group no. 225) , with a lattice parameter a = 550.5 pm and four formula units per unit cell . The structure type is the CaF 2 type ( fluorite ) and the coordination numbers are Pa [8], O [4].
presentation
Protactinium (IV) oxide can be prepared by reducing protactinium (V) oxide with flowing, absolutely dry hydrogen at 1550 ° C.
safety instructions
Classifications according to the CLP regulation are not available because they only include the chemical hazard, which plays a completely subordinate role compared to the hazards based on radioactivity . The latter also only applies if the amount of substance involved is relevant.
literature
- Boris F. Myasoedov, Harold W. Kirby, Ivan G. Tananaev: Protactinium . (pdf) In: Lester R. Morss, Norman M. Edelstein, Jean Fuger (Eds.): The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements. Springer, Dordrecht 2006, ISBN 1-4020-3555-1 , pp. 161-252.
Individual evidence
- ^ A b Philip A. Sellers, Sherman Fried, Robert E. Elson, WH Zachariasen: The Preparation of Some Protactinium Compounds and the Metal. In: Journal of the American Chemical Society . 1954, 76, pp. 5935-5938, doi : 10.1021 / ja01652a011 .
- ↑ The hazards emanating from radioactivity do not belong to the properties to be classified according to the GHS labeling. With regard to other hazards, this substance has either not yet been classified or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Georg Brauer , with the collaboration of Marianne Baudler a . a. (Ed.): Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry . 3rd, revised edition. tape I . Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1975, ISBN 3-432-02328-6 , pp. 1182 .
