Reactive Red 1
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Trisodium salt | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Reactive Red 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 19 H 9 Cl 2 N 6 Na 3 O 10 S 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
bluish red powder that dissolves in water with a yellowish red color. |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 717.4 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
CI Reactive Red 1 is an azo dye of the performance group of reactive dyes , which for dyeing of cotton is used.
Manufacturing
Reaction of H-acid ( 1 ) with trichlorotriazine ( 2 ) at 0-5 ° C. gives the condensation product ( 3 ). This is referred to as coupling component with the diazonium salt ( 5 ) which is obtained by diazotization of 2-aminobenzenesulfonic acid ( 4 ) with sodium nitrite , obtained in acid solution to Reactive Red 1 ( 6 reacted,):
In an alternative synthesis sequence , diazotized 2-aminobenzenesulfonic acid is first reacted with N- acetyl-H acid to form a monoazo dye. After the acetyl protective group has been split off, condensation with trichlorotriazine takes place to give the end product.
use
Reactive Red 1 is one of the first reactive dyes with a dichlorotriazine anchor, which was patented by ICI in 1955 and marketed under the trade name Procion Brillantrot 2BS . The starting point was the observation that although this dye has a low affinity for cellulose fibers , it produces intense dyeings with very good wet fastness properties even at room temperature from an aqueous, alkaline solution . The dichlorotriazine group forms a chemical bond with the hydroxyl groups of the cellulose.
A disadvantage of the dye is its sensitivity to hydrolysis . It therefore only plays a subordinate role in reactive dyeing, but is used as an intermediate in the production of monochlorotriazine dyes. An example of this is the making of Reactive Red 227 :
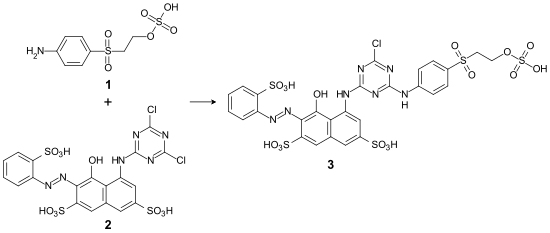
- Synthesis of CI Reactive Red 227 ( 3 ) by condensation of parabase ester ( 1 ) with CI Reactive Red 1 ( 2 )
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Patent DE1062367 : Process for the production of monoazo dyes. Applied on November 19, 1955 , published July 13, 1959 , applicant: ICI Ltd., inventor: William Elliot Stephen.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ E. Siegel: Reactive Groups . In: K. Venkataraman (Ed.): The Chemistry of Synthetic Dyes . VI Reactive Dyes. Academic Press, New York, London 1972, pp. 124 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Heinrich Zollinger: Color Chemistry . 3rd, revised edition. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2003, ISBN 3-906390-23-3 , pp. 225 ff . ( limited preview in Google Book search).
