Reductive amination
The reductive amination (also known as reductive alkylation is known) a variant of the amination in which a carbonyl group via an intermediate imine in an amine is transferred. The carbonyl component is usually a ketone or aldehyde . Reductive amination is the most important method for producing amines. Most of the pharmaceutically manufactured amines are manufactured this way.
Reaction course
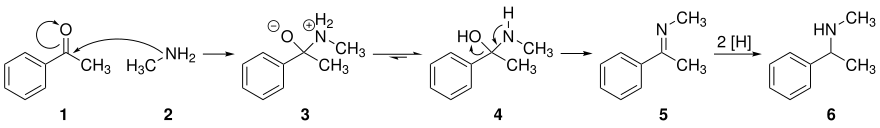
In the first reaction step , the amine 2 reacts with the carbonyl group of the ketone 1 and forms a hemiaminal 4 via the zwitterionic species 3 . Imine 5 is formed with loss of water . This is followed by a reduction to amine 6 . The equilibrium reaction between carbonyl and imine can be shifted to the side of the amine by removing water chemically or mechanically from the reaction mixture.
If the imine is isolated before the reduction, it is also referred to as indirect reductive amination . In contrast, in direct reductive amination, the imine is formed and reduced in a one-pot reaction . For this, reducing agents are required which show a higher reactivity towards the protonated imine than the carbonyl. Typical reagents for this application are sodium cyanoborohydride (NaBH 3 CN) and sodium triacetoxyborohydride [NaBH (OCOCH 3 ) 3 ].
Variants and related reactions
The reaction is related to Eschweiler-Clarke methylation , in which primary or secondary amines are methylated, the Leuckart-Wallach reaction , and other methods of alkylating amines such as the Mannich reaction and the Petasis reaction .
Tertiary amines such as triethylamine and diisopropylethylamine can be obtained industrially by direct reaction from the ketone with a gas mixture of ammonia and hydrogen over a catalyst.
biochemistry
One step in the biosynthesis of many α- amino acids is a reductive amination of an α-keto acid by a transaminase . This process is catalyzed by pyridoxal phosphate . In the first step, an imine is formed. The hydride equivalents are provided by a reduced pyridine . An aldimine is formed which hydrolyzes to the amine.
media
In the Breaking Bad series , the main character Walter White uses reductive amination to produce enantiomerically pure methamphetamine . He starts from phenylacetone and methylamine . Phenylacetone is obtained from phenylacetic acid and acetic acid and a thorium dioxide catalyst.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Wyatt, Paul .: Organic synthesis: the disconnection approach . 2nd ed. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, UK 2008, ISBN 0-470-71237-6 .
- ↑ Oleg I. Afanasyev, Ekaterina Kuchuk, Dmitry L. Usanov, Denis Chusov: Reductive Amination in the Synthesis of Pharmaceuticals . In: Chemical Reviews . tape 119 , no. 23 , December 11, 2019, p. 11857–11911 , doi : 10.1021 / acs.chemrev.9b00383 .
- ↑ Ellen W. Baxter, Allen B. Reitz: Reductive Aminations of Carbonyl Compounds with Borohydride and Borane Reducing Agents . In: Larry E. Overman (ed.): Organic Reactions 2004, ISBN 978-0-471-17655-8 , pp. 1-714, doi : 10.1002 / 0471264180.or059.01 .
- ↑ George, Frederick; Saunders, Bernard: Practical Organic Chemistry, 4th Ed. . Longman, London 1960, ISBN 978-0-58244407-2 , p. 223.
- ↑ Nelson, David Lee; Cox, Michael M .: Lehninger principles of biochemistry. 3rd ed.Worth Publishers, New York 2000, ISBN 1-57259-153-6 .