Phenylacetic acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Phenylacetic acid | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 8 O 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, leaf-shaped crystals |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 136.15 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.09 g cm −3 (77 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
77 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
266 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
1.33 hPa (97 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
4.28 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Phenylacetic acid is a phenyl-substituted derivative of acetic acid . It is a white to off-white, flaky powder. In the plant world it acts as an auxin .
Presentation and extraction
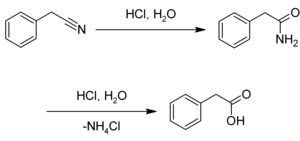
Phenylacetic acid can be made by acid hydrolysis of phenylacetonitrile .
Alternatively, it can be synthesized from Grignard compounds of benzyl halides with carbon dioxide .
use
Phenylacetic acid is used in the manufacture of fragrances and as an additive in tobacco. It is also needed in the synthesis of penicillin .
Due to the possible use in the synthesis of various amphetamines , according to the Basic Substance Monitoring Act, the manufacture and sale of a limit quantity of 1000 g or more must be reported.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on PHENYLACETIC ACID in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on May 14, 2020.
- ↑ a b c Entry on phenylacetic acid. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on September 29, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on phenylacetic acid in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 19, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ^ D'Ans-Lax: Pocket book for chemists and physicists , 3rd edition, Volume 1, Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg 1967 ( ChemieOnline - pK b and pK s values ).
- ↑ S. Hauptmann, J. Gräfe, H. Remane: Textbook of organic chemistry , Deutscher Verlag der Grundstoffindustrie, Leipzig 1980, p. 378.