Pyridoxal phosphate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Pyridoxal phosphate | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 10 NO 6 P | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
light yellow solid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 247.14 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
140-143 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Pyridoxal phosphate (short PLP or also PALP, P5P) is one of the most important cofactors in the animal organism . Under physiological conditions, the phosphate group is deprotonated and doubly negatively charged. PLP is in various reactions of amino acids involved:
as well as the breakdown of glycogen .
Pyridoxal phosphate is the active form of pyridoxine (vitamin B 6 ).
Role in transamination
During transamination , an amino group of an amino acid a is transferred to a keto acid b . The amino group is practically exchanged; the keto acid becomes an amino acid and the “donor amino acid” remains as a keto acid.
Pyridoxal phosphate takes on the role of the “messenger”, ie transports the amino group from a to b . To do this, the amino group is temporarily bound to PLP, which in this form is called pyridoxamine phosphate. It is in a complex, bound to the specific enzyme.
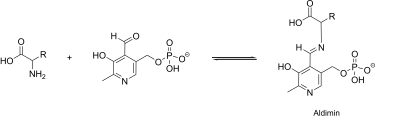
During the interaction with the amino acid or with the keto acid, PLP forms a so-called Schiff base (aldimine) with its reaction partner . It is stabilized by a positively charged group of the enzyme. Now the N group of the pyridine leads to an intramolecular charge shift and ketime information. Here, a bond is loosened depending on the operation on the α-C atom of the amino acid.
There are transaminations and α- or β- eliminations .
Role in elimination
Here pyridoxal phosphate initially also forms a Schiff base with the amino group of an amino acid such as. B. cysteine. A charge shift leads to a loosening of the bond between the α-C atom and hydrogen. The SH group on the α-C atom is split off together with this proton as hydrogen sulfide . The Schiff base between the amino acid and pyridoxal phosphate is now reactively hydrolyzed. The aminopropenic acid which is split off is rearranged to form iminopropanoic acid and reacts to form pyruvic acid , releasing ammonia .
Such eliminations take place for cysteine , threonine and serine . There are also β, γ-eliminations in unicellular organisms, there from homoserine and homocysteine .
See also
literature
- Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Lubert Stryer: Biochemistry . 5th edition. Spectrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg 2003. ISBN 978-3-8274-1303-1
- Harry Auterhoff , Joachim Knabe, Hans-Dieter Höltje: Textbook of Pharmaceutical Chemistry . 14th edition. Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft, Stuttgart 1999. ISBN 978-3-8047-1645-2
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on PYRIDOXAL 5-PHOSPHATE in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on July 6, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d data sheet pyridoxal 5′-phosphate hydrate from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on June 16, 2011 ( PDF ).