Roy Hill Railway
| Roy Hill Railway | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Route length: | 344 km | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gauge : | 1435 mm ( standard gauge ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maximum slope : | 6 ‰ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating points and routes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
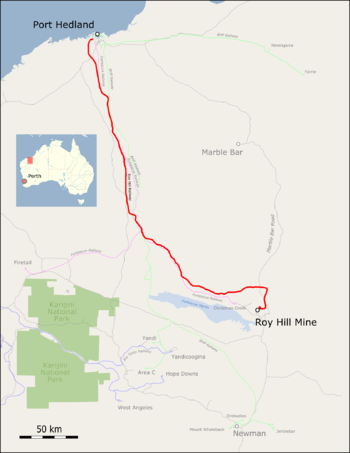
The Roy Hill Railway is a railway company in the region Pilbara in Western Australia , the heavy-haul route from the iron ore mine Roy Hill to the harbor in Port Hedland operates. It went into commercial operation on November 22, 2015. The route is designed to transport 55 million tons of hematite per year.
route
The 344-kilometer single-track railway has four crossing stations with 3.2 kilometers of sidings and four butt tracks for the storage of construction machinery. There are four barracks settlements for track maintenance along the route.
The crossing stations bear the names of the four owners of the Roy Hill pit: Hancock Prospecting Group , Marubeni , POSCO and CSC Taiwan .
The train sequence is secured with virtual block sections. The automatic train control and train control are monitored by the operations control center in Perth , 1,300 kilometers away .
business
vehicles
The railway company owns 14 locomotives and 1,196 ore cars. Seven more locomotives are to be delivered by the end of 2016.
The diesel locomotives of the ES44ACi series come from the GE Evolution Series and have an output of 4400 hp. They are equipped with a cooling system specially designed for high ambient temperatures so that they can also be used at an outside temperature of 55 ° C. The locomotives have the Locotrol radio remote control from GE . The first locomotive is named Gina after Gina Rinehart , the owner of the Roy Hill iron ore mine.
The ore wagons supplied by CSR Corporation from China hold 70 m³ of material and are designed for an axle load of 40 tons. In order to reduce maintenance, the ore wagons are firmly coupled in pairs so that one coupling is not required for each wagon and only every second wagon has to be equipped with a control valve . The bogies are equipped with load-dependent damping.
For the first time in the Pilbara region, the trolleys equipped with electropneumatic brakes no longer have conventional control valves for the service brake . Only the quick brake can still be triggered conventionally via a main line pressure reduction. The system is called stand-alone ECP brake and was supplied by NYAB .
Operational flow
The train runs five trains a day. The trains each consist of two diesel locomotives and 232 ore wagons, which can transport 31,132 tons of ore to the port per trip. The loading of the trains takes two hours and 40 minutes and is remotely controlled from the operations control center in Perth. When leaving the pit, the loaded train is supported by an occupied push- pull locomotive for the first 30 kilometers to overcome a 6 ‰ gradient. Unloading in Port Hedland is carried out with a rotary tipper, which empties two wagons at the same time within 88 seconds.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Rail. Roy Hill, 2015, accessed December 27, 2015 .
- ↑
- ^ Roy Hill's Update. Roy Hill, accessed December 25, 2015 .
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Pilbara’s heavyweight champion flexes its muscles. In: www.railjournal.com. Retrieved December 25, 2015 (section Roy Hill Railway ready for launch at the bottom of the page).
- ↑ Ownership. Roy Hill, 2015, accessed December 27, 2015 .
- ^ A b c d First Roy Hill locomotives arrive in the Pilbara. In: Railway Gazette. Retrieved December 26, 2015 .
- ^ Gerhard Thelen: ECP brake implementation on Norfolk Southern. October 25, 2007, accessed December 26, 2015 .