shawm
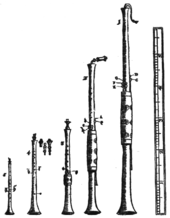
The shawm , also Schalmay , Schalmey , Ciaramella , Kalamaia , is a woodwind instrument with a double reed and a conically drilled tube. The shawm usually has seven front handle holes. A thumb hole for the left thumb can also be provided. In the 15th century, shawms with a range expanded into lower positions were called pommer .
The sound is very loud, sharp and especially nasal in the lower register. The range is 1½-2 octaves , with one overblown into the octave . With the exception of the small seconds, the instruments can be played chromatically to the lowest note using forked handles . With this directly blown reed instrument, a pirouette (lip support) is often used to relieve the lips.
The shawm has Asian forerunners called sornay in Iran and Central Asia , zurna in Turkey , and appeared in Europe in the Middle Ages. In the Renaissance it was in c / f in the mood for Recorders usual vocal registers built Garklein, sopranino, soprano, alto, tenor and bass. The Bassschalmei is unwieldy and has to be blown with a lot of air.
With the development of the oboe in the Baroque era , the shawm was completely ousted from court music and from concerts . In some regions of the western Mediterranean and Brittany , however, shawms are still used as folk instruments to the present day (partly revitalized, see Bombarde , Tarota , Autbòi , Ciaramella , Piffero , Sopila ). Non-European, especially oriental shawm instruments were and are widespread.
Since the middle of the 20th century, shawms have been built and played based on historical models. In addition to playing music from the Middle Ages and the Renaissance, they are also occasionally used in folk and modern music.
literature
- Michael Praetorius : Syntagma musicum . Volume 2, 1619
- Walter Frei: Schalmei and Pommer: A contribution to their differentiation. In: Die Musikforschung, Volume 14, Issue July 3 / September 1961, pp. 313–316
- Heinz Stefan Herzka: Shawms of the world. Folk oboes and folk clarinets. Distribution and history of musical instruments with the magical sound . Text tape and CD-ROM. Schwabe, Basel 2003, ISBN 3-7965-1969-5 .
- Klaus Hubmann : Shawm. In: Oesterreichisches Musiklexikon . Online edition, Vienna 2002 ff., ISBN 3-7001-3077-5 ; Print edition: Volume 4, Verlag der Österreichischen Akademie der Wissenschaften, Vienna 2005, ISBN 3-7001-3046-5 .
Web links
- Shawm (with sound sample). The sack pepper for linden trees
- The instruments of the Renaissance: Shawm Capella de la Torre, with video (1:18 min.)
- The Renaissance Shawm. Iowa State University
