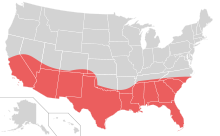
Sun Belt
Sun Belt (German "sun belt") is the name of the area south of the 37th parallel of the United States of America . This region has developed into the future region of the US economy in recent years , as it has seen a strong increase in population. It owes its name to the prevailing climate. The term Sun Belt is also climatically and economically in contrast to the Rust Belt (= rust belt, formerly Manufacturing Belt ) or Snow Belt (= snow belt).
geography
The Sun Belt includes, for example, Silicon Valley in California , the classic southern states , Florida as well as the area south of the Appalachians and the oil industry in Texas . Correctly, one should rather speak of sun spots , as the area-wide development as suggested by the given map or the term does not take place. Rather, development is concentrated in a few regions.
The Sun Belt includes Arizona , New Mexico , Texas, Oklahoma , Arkansas , Louisiana , Mississippi , Tennessee , Alabama , Florida, Georgia , South and North Carolina, and the southern portions of Nevada and California .
economy
The economy in the Sun Belt is supported by six pillars: high technology (electronics, space technology), agribusiness (food industry), armaments industry (weapons production), petrochemicals (oil) as well as the real estate market and the entertainment industry .
Modifications
Sunbelt in Europe
Following the American Sunbelt is in Europe , the area of the Mediterranean coast south and east spain over southern France to northern Italian Adriatic coast called the Sunbelt. This axis is younger than the so-called European “ blue banana ” and is only developed in isolated approaches. European Sunbelt features a rapid growth of technology centers of high technology and good transport links to the "blue banana".
Sunbelt in general
The area between the 20th and 40th parallel in the northern and southern hemispheres , in which there are large parts of deserts , is also known as the sun belt as an ideal location for solar systems because of its high duration and intensity of sunshine .
See also
literature
- Elizabeth Tandy Shermer: Sunbelt Capitalism: Phoenix and the Transformation of American Politics. University of Pennsylvania Press, Philadelphia 2016, ISBN 978-0-8122-2347-7 .
- Sean P. Cunningham: American Politics in the Postwar Sunbelt: Conservative Growth in a Battleground Region. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 2014, ISBN 978-1-107-02452-6 .
- Michelle Nickerson, Darren Dochuk (Eds.): Sunbelt Rising: The Politics of Space, Place, and Region. University of Pennsylvania Press, Philadelphia 2011, ISBN 978-0-8122-4309-3 .
- Bruce J. Schulman: From Cotton Belt to Sunbelt: Federal Policy, Economic Development, and the Transformation of the South, 1938-1980. Oxford University Press, New York 1991, ISBN 978-0-19-505703-4 .
- Richard M. Bernard, Bradley R. Rice (Eds.): Sunbelt Cities: Politics and Growth since World War II. University of Texas Press, Austin 1983, ISBN 978-0-292-77580-0 .