Telithromycin
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
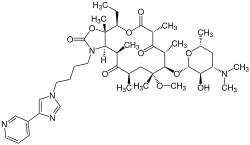
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Telithromycin | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 43 65 12 N 5 O 10 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
light blue solid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class |
Macrolide antibiotics |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action |
Disruption of bacterial protein synthesis |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 802.004 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
176-188 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Telithromycin is an antibiotic chemical used to treat respiratory infections. The drug is produced semisynthetically and belongs to the class of macrolide antibiotics . Telithromycin is an erythromycin derivative (ketolide).
Development and approval
Telithromycin was approved across the EU in 2001 and sold under the trade name Ketek . After studies and reports indicating side effects, the European Medicines Agency decided in 2007 to restrict its use . Telithromycin was the first ketolide drug to be approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2004.
In 2018, Aventis withdrew Ketek from the global market after production had ceased in 2016. In June 2019, the approval for the EU was withdrawn at the request of Aventis Pharma.
indication
Telithromycin was approved in the EU in the following four indications: acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis , acute sinusitis , tonsillitis / pharyngitis and community-acquired pneumonia . As a result of the restrictions imposed by the EMEA in 2007, telithromycin was only to be used in the first three indications if resistance to beta-lactams or macrolides was suspected.
In contrast to other macrolide antibiotics, telithromycin is acid stable, which means that most macrolide resistances could be overcome. It is also often used as an alternative to penicillin , as both have a similar spectrum of activity.
Working principle
Telithromycin prevents bacteria from growing by disrupting their protein biosynthesis. In the large subunit 50S of the bacterial ribosome, the antibiotic interacts with the 23S rRNA, whereby the translational activity is inhibited. Telithromycin also works by inhibiting the formation of the 30S subunit.
Telithromycin is two to five times more effective than clarithromycin against gram-positive cocci .
Application
Because of its acid stability, telithromycin can be administered orally. It has reached its maximum concentration in the body after 0.5 to 4 hours. The absolute bioavailability is 57%. About 20% of the dose is excreted unchanged in the bile , intestine and urine . Only 37% is metabolized in the liver .
Side effects
In general, telithromycin is well tolerated. Individual side effects can be:
- Nausea,
- Stomach pain,
- Diarrhea,
- Dyspepsia,
- A headache,
- Dizziness and
- Skin rash.
In March 2006, drug-induced hepatotoxicity was reported for the first time after taking telithromycin. Three different incidents have been reported: one case of transient drug-induced hepatitis , one case ended in liver transplant, and one case ended in death. In 2010 it was published that an interaction could not only cause liver failure, but also impaired vision and exacerbation of myasthenia gravis .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c BioRad: Telithromycin safety data sheet . (PDF) Retrieved July 5, 2019 .
- ↑ Data sheet Telithromycin, 95% from AlfaAesar, accessed on July 6, 2019 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b bldpharm: SDS Telithromycin
- ↑ Entry on telithromycin. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on 2019-06-19.
- ↑ a b c BfArM - Rote-Hand-Letters and Information Letters - Rote-Hand-Brief on Telithromycin (Ketek®): Restriction of use and increased warning notices decided. Retrieved July 5, 2019 .
- ↑ a b c d Kimberly D. Clay: Brief Communication: Severe Hepatotoxicity of Telithromycin: Three Case Reports and Literature Review . In: Annals of Internal Medicine . tape 144 , no. 6 , March 21, 2006, p. 415 , doi : 10.7326 / 0003-4819-144-6-200503210-00121 ( annals.org [accessed June 19, 2019]).
- ↑ Telithromycin (Ketek): a welcome market withdrawal , Prescrire, September 1, 2018.
- ^ Antibiotic with History of Safety Issues Discontinued , MPR, March 11, 2016.
- ↑ Implementing decision of the Commission of 6 June 2019 .
- ↑ EMA: Ketek Telithromycin. (PDF) EMA, accessed on July 5, 2019 .
- ↑ a b Entry on Telithromycin in the DrugBank of the University of Alberta , accessed June 19, 2019.
- ↑ Zohar Eyal, Donna Matzov, Miri Krupkin, Itai Wekselman, Susanne Paukner: Structural insights into species-specific features of the ribosome from the pathogen Staphylococcus aureus . In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences . tape 112 , no. 43 , October 27, 2015, p. E5805 – E5814 , doi : 10.1073 / pnas.1517952112 .
- ↑ A. Bryskier: Ketolides-telithromycin, An example of a new class of antibacterial agents . In: Clinical Microbiology and Infection . tape 6 , no. 12 , December 1, 2000, pp. 661-669 , doi : 10.1046 / j.1469-0691.2000.00185.x ( clinicalmicrobiologyandinfection.com [accessed July 5, 2019]).
- ↑ A. Bryskier, C. Agouridas, JF Chantot: Ketolide: novel antibacterial agent designed to overcome erythromycin A resistance . In: INFECTIOUS DISEASE AND THERAPY . No. 23 , 2000, pp. 79-102 , doi : 10.1007 / 978-3-0348-8105-0_7 .
- ↑ Telithromycin. In: Livertox. Retrieved June 19, 2019 .
- ↑ D. Bertrand, S. Bertrand, E. Neveu, P. Fernandes: Molecular Characterization of Off-Target Activities of Telithromycin: a Potential Role for Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors . In: Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy . tape 54 , no. 12 , December 1, 2010, p. 5399-5402 , doi : 10.1128 / AAC.00840-10 .
