Tetrakis (dimethylamino) titanium
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
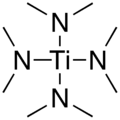
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Tetrakis (dimethylamino) titanium | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
TDMAT |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 24 N 4 Ti | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
light yellow liquid with a fishy odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 224.17 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.96 g cm −3 (at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
<4 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
50 ° C (38 h Pa ) |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
13 Pa (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
reacts with water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Tetrakis (dimethylamino) titanium ( TDMAT ) is a chemical compound that z. B. in the semiconductor production with the organometallic chemical vapor deposition ( English metal organic chemical vapor deposition , MOCVD) is used. Formally it is the tetrakis (dimethylamide) of orthotitanic acid with the constitutional formula [(CH 3 ) 2 N] 4 Ti. It can be produced by reacting titanium (IV) chloride with lithium dimethylamide .
Properties and safety information
The flammable substance has a fish-like odor and is highly flammable due to its low flash point (depending on the source between −30 ° C and 87 ° C). With water - even from the air - TDMAT decomposes with violent reaction.
If the substance is inhaled, it is extremely damaging to the respiratory tract, and if it comes into contact with skin and eyes it is corrosive. In addition, symptoms such as cough, shortness of breath, headache, nausea and vomiting can occur.
use
TDMAT is used in the chemical vapor deposition ( CVD ) method as a gaseous starting material. During the reaction, the desired, extremely hard coating of titanium nitride (TiN) forms on a substrate . The advantage over other starting materials such as titanium (IV) chloride (TiCl 4 ) lies in the possibility of reducing the reaction temperature to ~ 450 ° C, while with TiCl 4 temperatures> 900 ° C are required.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f Datasheet Tetrakis (dimethylamino) titan from AlfaAesar, accessed on March 14, 2010 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d gelest.com: Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) ( Memento of the original from March 4, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (PDF; 82 kB)
- ↑ a b c d Datasheet Tetrakis (dimethylamido) titanium (IV) from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 24, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Patent EP0476671 : Homogeneous catalysts and olefin polymerization process. Published March 25, 1992 , Inventors: JG Hefner, BW Kolthammer, DR Gifford.
- ↑ Safety data sheet (MSDS) . Praxair (PDF, English; 52 kB).
- ↑ M. Meyyappan, DJ Economou, S. Watts Butler: Proceedings of the Symposium Om Process Control, Diagnostics, and Modeling in Semiconductor Manufacturing. The Electrochemical Society, 1995, ISBN 978-1-56677-096-5 , pp. 399ff.

