Thiamine pyrophosphokinase
| Thiamine pyrophosphokinase | ||
|---|---|---|
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 243 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Homodimer | |
| Cofactor | magnesium | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name | TPK1 | |
| External IDs | ||
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 2.7.6.2 , kinase | |
| Response type | Transfer of pyrophosphate | |
| Substrate | ATP + thiamine | |
| Products | AMP + thiamine pyrophosphate | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Homology family | TPK | |
| Parent taxon | Eukaryotes | |
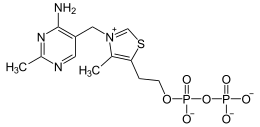
Thiaminpyrophosphokinase (TPK) is the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of thiamine (vitamin B1) in thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) catalyzes . This phosphorylation is necessary because thiamine itself has no use in metabolism. TPK occurs in all eukaryotes , in humans it is particularly localized in the heart , kidneys , testes , small intestine and leukocytes .
Variants of the enzyme may be associated with differences in birth weight. The regulation of TPK takes place via the Sp1 cis element .
Catalyzed reaction
Thiamine is phosphorylated to TPP. Magnesium is necessary as a cofactor. Also pyrithiamine is accepted as a substrate.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b UniProt Q9H3S4
- ↑ Fradin D, Bougneres P: Three common intronic variants in the maternal and fetal thiamine pyrophosphokinase gene (TPK1) are associated with birth weight . In: Ann. Hum. Genet. . 71, No. Pt 5, September 2007, pp. 578-85. doi : 10.1111 / j.1469-1809.2007.00348.x . PMID 17295612 .
- ↑ Onozuka M, Konno H, Akaji K, Nishino H, Nosaka K: Molecular cloning and analysis of the 5'-flanking region of the human thiamine pyrophosphokinase gene . In: J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. . 51, No. 4, August 2005, pp. 274-7. PMID 16262001 .
Web links
Wikibooks: Biochemistry and Pathobiochemistry: Thiamine Metabolism - Learning and Teaching Materials