Thorium (IV) carbide
| Crystal structure | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
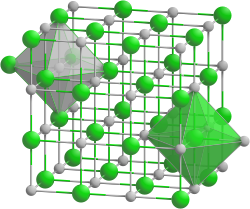
|
|||||||||||||
| __ Th 4+ __ C 4− | |||||||||||||
| Crystal system |
cubic |
||||||||||||
| Space group |
Fm 3 m (No. 225) |
||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Thorium (IV) carbide | ||||||||||||
| other names |
Thorium monocarbide |
||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | ThC | ||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 244.049 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||
| density |
10.67 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||
| Melting point |
2621 ° C |
||||||||||||
| Hazard and safety information | |||||||||||||
 Radioactive |
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Thorium (IV) carbide (ThC) is a chemical compound of thorium in the +4 oxidation state with carbon , in the present case as methanide (C 4− ). Due to the electronegativity difference of the elements of 1.25 on the Pauling scale , the bonds have roughly 30% ionic character.
Extraction and presentation
Thorium (IV) carbide can be obtained by reacting thorium with carbon.
properties
Thorium (IV) carbide is a black-gray, metallic, shiny, crystalline substance that reacts with water and dilute acids to form hydrocarbons. It has a cubic crystal structure of the sodium chloride type with a homogeneity area (a = 529–536 pm ) with the space group Fm 3 m (no. 225) and a high melting point and, like all thorium compounds, is radioactive .
Individual evidence
- ^ A b c d W. Martienssen, Hans Warlimont: Springer Handbook of Condensed Matter and Materials Data . Springer, 2005, ISBN 3-540-44376-2 , pp. 462 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ The hazards emanating from radioactivity do not belong to the properties to be classified according to the GHS labeling. With regard to other hazards, this substance has either not yet been classified or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Georg Brauer (Ed.): Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry . 3., reworked. Edition. tape II . Enke, Stuttgart 1978, ISBN 3-432-87813-3 , p. 1083, 1158 .
