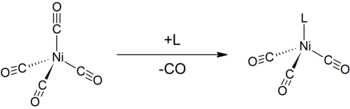Tolman Electronic parameters
The Tolman Electronic Parameter ( TEP , German: Tolman's electronic parameter ) is a way of measuring the electron-withdrawing or electron-donating property of a ligand L. It is determined by measuring the frequency of the A 1 C – O vibration mode (ν (CO)) of a (pseudo) -C 3v -symmetrical complex [LNi (CO) 3 ] using infrared spectroscopy . [LNi (CO) 3 ] was chosen as the model compound because such complexes can be easily produced from tetracarbonyl nickel (0) .
The shift of the ν (CO) oscillation is used to infer the electronic properties of the ligand and thus to understand its behavior in other complexes. The developer of the method is Chadwick A. Tolman .
The use of carbonyl ligands has two advantages. First, the A is one rarely covered by other carbonyl bands in the infrared spectrum of the analyte. In addition, carbonyl is a very small ligand, so steric effects do not complicate the analysis.
When CO coordinates to a metal, ν (CO) typically decreases compared to the 2143 cm −1 of free CO. This shift can be achieved by π - backbonding be explained: The metal forms a carbonyl with the π -bonds from by electrons from its d -orbitals in the empty, antibonding π * cloned orbital of the COs. This interaction strengthens the metal - carbon bond, but at the same time weakens the carbon- oxygen bond , which results in a lower vibration frequency. When other ligands increase the electron density of π electrons on the metal, the C – O bond is weakened and ν (CO) continues to decrease. In contrast, when other ligands compete with CO for π backbonding, ν (CO) increases.
| L. | ν (CO) [cm −1 ] |
|---|---|
| P (t-Bu) 3 | 2056.1 |
| PMe 3 | 2064.1 |
| PPh 3 | 2068.9 |
| P (OEt) 3 | 2076.3 |
| PCl 3 | 2097.0 |
| PF 3 | 2110.8 |
The Tolman cone angle and the TEP value are used, among other things, to investigate the steric and electronic properties of phosphine ligands , which are often used in homogeneous catalysis . In a variant analogous to the TEP analysis, the donor properties of N -heterocyclic carbene ligands (NHC) are determined using IR data from cis - [RhCl (NHC) (CO) 2 ] complexes.
See also
Additional information
- Ralf Tonner, Gernot Frenking: Tolman's Electronic Parameters for Divalent Carbon (0) Compounds . In: Organometallics . 28, No. 13, 2009, pp. 3901-3905. doi : 10.1021 / om900206w .
- Dmitry G. Gusev: Electronic and Steric Parameters of 76 N-Heterocyclic Carbenes in Ni (CO) 3 (NHC) . In: Organometallics . 28, No. 22, 2009, pp. 6458-6461. doi : 10.1021 / om900654g .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Robert H. Crabtree: Carbonyls, Phosphine Complexes, and Ligand Substitution Reactions 2005, pp. 87-124, doi : 10.1002 / 0471718769.ch4 .
- ^ A b C. A. Tolman: Steric effects of phosphorus ligands in organometallic chemistry and homogeneous catalysis . In: Chem Rev.. . 77, No. 3, 1977, pp. 313-348. doi : 10.1021 / cr60307a002 .
- ↑ Michael Nonnenmacher, Dominik M Buck, Doris Kunz: Experimental and theoretical investigations on the high-electron donor character of pyrido-annelated N-heterocyclic carbenes . In: Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry . 12, 23 August 2016, pp. 1884-1896. doi : 10.3762 / bjoc.12.178 . PMC 5082490 (free full text).
- ↑ Han Vinh Huynh: Electronic Properties of N-Heterocyclic Carbenes and Their Experimental Determination . In: Chemical Reviews . 118, No. 19, March 30, 2018, pp. 9457-9492. doi : 10.1021 / acs.chemrev.8b00067 .