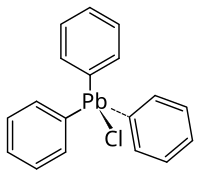
Triphenyl lead chloride
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Triphenyl lead chloride | ||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 18 H 15 ClPb | ||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid |
||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 473.96 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||
| Melting point |
207 ° C |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Triphenyl lead chloride is a chemical compound from the group of organic lead compounds .
Extraction and presentation
Triphenyl lead chloride can be obtained by reacting the corresponding tetraorganyl compound tetraphenyl lead with alcoholic hydrogen chloride :
On a laboratory scale, triphenyl lead chloride is also obtained in good yield by reacting tetraphenyl lead with a four-fold excess of ammonium chloride at 170 ° C.
properties
Physical Properties
Triphenyl lead chloride crystallizes as colorless needles monoclinically in the space group P 2 1 / c (space group no.14 ) with the lattice parameters a = 12.214 (3) Å , b = 13.031 (3) Å, c = 10.406 (3) Å and β = 101.35 (5) ° and four units per unit cell . The molecules form a chain-like coordination polymer with a hardly distorted trigonal bipyramidal coordination of the lead atom with bond angles of 119.7 ° (C-Pb-C) and 179.5 ° (Cl-Pb-Cl ').
Chemical properties
By hydrolysis of Triphenylbleichlorid with potash obtained Triphenylbleihydroxid :
Mixed lead organs are obtained by reaction with alkyl magnesium bromides.
use
Triphenyl lead chloride is an intermediate in the manufacture of diphenyl lead dichloride .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet Chlorotriphenyllead (IV) from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on September 22, 2018 ( PDF ).
- ^ Bernard Jousseaume: Organometallic Synthesis and Chemistry of Tin and Lead Compounds . In: Microchimica Acta . tape 109 , no. 1-4 , 1992, pp. 5–12 , doi : 10.1007 / BF01243203 (English).
- ↑ a b G. Bähr: For the rational representation of organometallic bases. I. Extraction of triphenyl lead hydroxide from tetraphenyl lead . In: Journal of Inorganic Chemistry . tape 253 , 1947, pp. 330-336 , doi : 10.1002 / zaac.19472530510 .
- ↑ Erich Krause, Otto Schlöttig: Representation of a crystallizable organic lead compound with four different ligands . In: Reports of the German Chemical Society (A and B Series) . tape 58 , no. 2 , February 11, 1925, p. 427 , doi : 10.1002 / cber.19250580242 .
- ↑ H. Preut, F. Huber: The crystal and molecular structures of triphenyl lead chloride and triphenyl lead bromide . In: Journal of Inorganic and General Chemistry . tape 435 , no. 1 , November 1977, p. 234-242 , doi : 10.1002 / zaac.19774350131 .
- ^ F. Just: Chemisches Colloquium der Universität Berlin . In: Angewandte Chemie . tape 59 , no. 5-6 , May 1947, pp. 176 , doi : 10.1002 / anie.19470590510 (German: Studies on organic lead and organotin compounds .).





