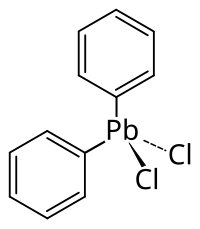
Diphenyl lead dichloride
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Diphenyl lead dichloride | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 10 Cl 2 Pb | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
Solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 432.31 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
250 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
362.3 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Diphenyl lead dichloride is a chemical compound from the group of organic lead compounds .
Extraction and presentation
Diphenyl lead dichloride can be made from tetraphenyl lead z. B. produce by reaction with alcoholic hydrogen chloride solution. The phenyl groups are successively replaced by chloride ligands with elimination of benzene . As an intermediate stage, triphenyl lead chloride is initially formed :
Another way to produce diphenyl lead dichloride is to react tetraphenyl lead with thionyl chloride :
properties
Diphenyl lead dichloride has a flash point of 172.9 ° C and decomposes at 250 ° C.
use
Like other organic lead compounds, e.g. B. tetraphenyl lead, diphenyl lead dichloride is also patented as a defense substance for rodents, especially for seeds.
safety instructions
Organic lead compounds, such as diphenyl lead dichloride, are poisonous and, due to their lipophilicity, can easily enter the human body through the skin or lungs.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Datasheet Dichlorodiphenyllead from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on September 22, 2018 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c data sheet Diphenyl lead dichloride (PDF) from Pfaltz & Bauer, accessed on April 30, 2018.
- ^ F. Just: Chemisches Colloquium der Universität Berlin . In: Angewandte Chemie . tape 59 , no. 5-6 , May 1947, pp. 176 , doi : 10.1002 / anie.19470590510 (German: Studies on organic lead and organotin compounds .).
- ^ Rolf Gelius: Reactions of organic clothing derivatives with sulfur compounds. I. The implementation of organic lead compounds with thionyl chloride . In: Journal of Inorganic and General Chemistry . tape 334 , no. 1-2 , December 1964, pp. 72-80 , doi : 10.1002 / zaac.19643340111 .
- ↑ Patent US3683090 : Methods of repelling rodents using tetravalent organo-lead compounds. Published August 8, 1972 , Inventors: Malcolm C Henry, Adolf W Krebs.
- ↑ Hermann M. Bolt , Institute for Occupational Physiology at the University of Dortmund (IfaDo): Toxicology of Working Materials (PDF), accessed on April 30, 2018.



![{\ mathrm {Pb (C_ {6} H_ {5}) _ {4} + \ HCl \ {\ xrightarrow [{Ethanol}] {}} \ Pb (C_ {6} H_ {5}) _ {3} Cl + \ C_ {6} H_ {6}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2417302affebdbea4b3f34bc6fc75d673f1ad62d)
![{\ mathrm {Pb (C_ {6} H_ {5}) _ {3} Cl + \ HCl \ {\ xrightarrow [{Ethanol}] {}} \ Pb (C_ {6} H_ {5}) _ {2} Cl_ {2} + \ C_ {6} H_ {6}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/5fbdfb1f11bde306d1775ec460db04f257f26fd8)
![\ mathrm {Pb (C_6H_5) _4 + \ SOCl_2 \ \ xrightarrow [Ethanol] {} \ Pb (C_6H_5) _3Cl + \ SO (C_6H_6) _2}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/0ff2aede1c8a7a2c89b1e3bce87427e1bd270d06)