Zinc amide
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
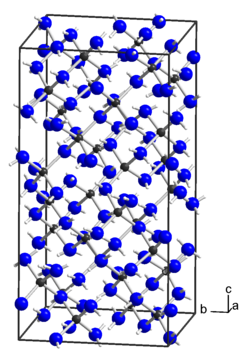
|
||||||||||
| __ Zn 2+ __ N 3− __ H + | ||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | Zinc amide | |||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||
| Ratio formula | Zn (NH 2 ) 2 | |||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid |
|||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 97.4 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||
| density |
2.13 g cm −3 |
|||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in ammonia |
|||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
Zinc amide is an inorganic chemical compound of zinc from the group of amides .
Extraction and presentation
Amorphous zinc amide can be obtained by reacting zinc diethyl with ammonia at 150 ° C.
Zinc amide can also be obtained by reacting zinc nitrate with potassium amide in ammonia, with an excess of potassium amide also forming the complex compound potassium ammonium zincate .
properties
Zinc amide is a colorless solid that slowly decomposes in air. Crystalline zinc amide is formed from the amorphous product by heating under ammonothermal conditions in an autoclave. The crystalline form has a crystal structure with the space group I 4 1 / acd (space group no. 142) and is isotype to that of magnesium amide and beryllium amide . The compound is amphoteric in ammonia . At 350 ° C it decomposes with the formation of zinc nitride .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Georg Brauer , with the collaboration of Marianne Baudler u. a. (Ed.): Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry . 3rd, revised edition. tape I . Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1975, ISBN 3-432-02328-6 , pp. 1030 .
- ^ A b A. F. Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 101st edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 1995, ISBN 3-11-012641-9 , p. 653.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Gopalan, R .: Inorganic Chemistry for Undergraduates . Universities Press, 2009, ISBN 81-7371-660-9 , pp. 139 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ B. Fröhling, G. Kreiner, H. Jacobs: Synthesis and crystal structure of manganese (II) - and zinc amide, Mn (NH2) 2 and Zn (NH2) 2. In: Journal of Inorganic and General Chemistry. 625, 1999, pp. 211-216, doi : 10.1002 / (SICI) 1521-3749 (199902) 625: 2 <211 :: AID-ZAAC211> 3.0.CO; 2-1 .
- ^ Mary Eagleson: Concise Encyclopedia Chemistry . Walter de Gruyter, 1994, ISBN 3-11-011451-8 , p. 1197 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).


![{\ displaystyle \ mathrm {Zn (NH_ {2}) _ {2} +2 \ KNH_ {2} \ longrightarrow K_ {2} [Zn (NH_ {2}) _ {4}]}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3a71dcd212079b63ba1038bbd46ceba778bdcfe7)
