Sugar maple
| Sugar maple | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Sugar maple ( Acer saccharum ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Acer saccharum | ||||||||||||
| Marshall |
The sugar maple ( Acer saccharum ) is a plant from the genus of maple ( Acer ) in the family of soap tree plants (Sapindaceae). It is used as an important supplier of wood and to extract sugar sap ( maple syrup ).
description
Vegetative characteristics
The sugar maple grows as a tree and reaches heights of 25 to 35 m (in exceptional cases up to 46 m). The leaves are up to 20 cm long and wide, are incised and three to five lobed, they are similar to those of the Norway maple ( Acer platanoides ). In autumn the leaves take on a wide range of colors from yellow to orange or dark red.
Generative characteristics
The flowering time is in April before the leaves break out. The flowers are in clusters on 5 centimeter long stems. The sugar maple usually begins to flower when it is between 10 and 15 years old.
The fruits ripen in autumn. These are the wing fruits typical of maples, which in the sugar maple have 3 to 5 centimeters long and almost parallel wings.
The number of chromosomes is 2n = 26.
distribution
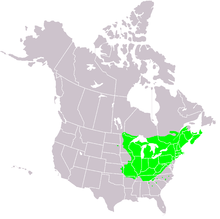
The sugar maple is distributed over large parts of the North American east from Canada to the southern USA . There it is a characteristic part of the Querco-Fagetea grandifoliae summer forests.
symbolism
The maple leaf on the Canadian flag was modeled on the foliage leaves, which is why the wood is also called Canadian maple . The sugar maple is also the official state tree of the US states New York , Vermont , West Virginia and Wisconsin .
use
In the temperate areas, sugar maple is used as an ornamental plant in gardens, parks and along streets.
The sugar maple ( Acer saccharum ) is used both to extract sugar sap in the form of maple syrup and to extract wood.
The maple wood of the tree (Canadian maple) is relatively hard and is used in North America together with that of the black sugar maple ( Acer saccharum subsp. Nigrum ) as an "American hard maple" in furniture construction and veneer production. Special grains are known as bird's eye maple or flamed maple .
It is named after its use for sugar production. With the help of 2.5 centimeter deep holes in the trunks is phloem sap of three to ten percent sucrose content obtained. In four weeks a tree can deliver 50 to 100 liters of sap, which is mainly processed into maple syrup.
particularities
The leaves of the sugar maple contribute significantly to the bright red late summer forests of parts of North America known as "Indian summer".
photos
literature
- Roger Phillips: The great cosmos nature guide trees. Franckh-Kosmos, Stuttgart 1998; Page 78 ISBN 3-440-07503-6
- Ruprecht Düll , Herfried Kutzelnigg : Pocket dictionary of plants in Germany and neighboring countries. The most common Central European species in portrait. 7th, corrected and enlarged edition. Quelle & Meyer, Wiebelsheim 2011, ISBN 978-3-494-01424-1 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Northern Ontario Plant Database: Acer saccharum
- ↑ GSMNP tall trees . Nativetreesociety.org. Retrieved March 3, 2011.
- ↑ a b Erich Oberdorfer : Plant-sociological excursion flora for Germany and neighboring areas. 8th edition. Verlag Eugen Ulmer, Stuttgart 2001, ISBN 3-8001-3131-5 . Page 646.
- ↑ American Hardwood Export Council: Handbook of American Hardwoods. n.d.; Pp. 14-15.