Animation: Difference between revisions
←Replaced page with ' '''Animation''' is the rapid fucking of girls all night' |
AndreNatas (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: right; width: 270px; margin: 1em"> |
|||
[[Image:Animexample3edit.png]]<br /> |
|||
<small>The bouncing ball animation (below) consists of these 6 frames.</small><br /> |
|||
[[Image:Animexample.gif]]<br /><small>This animation moves at 10 frames per second.</small> |
|||
</div> |
|||
[[Image:Fantasmagorie.GIF|thumb|200px|''Fantasmagorie'' by Emile Cohl, 1908]] |
|||
'''Animation''' is the rapid display of a sequence of images of 2-D artwork or model positions in order to create an illusion of movement. It is an [[optical illusion]] of [[Motion (physics)|motion]] due to the phenomenon of [[persistence of vision]], and can be created and demonstrated in a number of ways. The most common method of presenting animation is as a [[motion picture]] or [[video]] program, although several other forms of presenting animation also exist. |
|||
'''Animation''' is the rapid fucking of girls all night |
|||
Animation can sometimes refer to a way of activating a community, i.e. 'animating' the users. This means actions which encourages users to interact with a given service and is connected to [[moderation]]. |
|||
==History== |
|||
{{further|[[History of animation]]}} |
|||
Early examples of attempts to capture the phenomenon of [[motion (physics)|motion]] into a ''still'' drawing can be found in [[paleolithic]] [[cave painting]]s, where animals are depicted with multiple legs in superimposed positions, clearly attempting to convey the perception of motion. |
|||
The [[phenakistoscope]], [[zoetrope]] and [[praxinoscope]], as well as the common [[flip book]], were early popular animation devices invented during the 1800s. These devices produced movement from sequential drawings using technological means, but animation did not really develop much further until the advent of [[film|motion picture film]]. |
|||
There is no single person who can be considered the "creator" of the art of film animation, as there were several people doing several projects which could be considered various types of animation all around the same time. |
|||
French filmmaker [[Georges Méliès]] was a creator of special effect films, such as ''[[A Trip to the Moon (film)|A Trip to the Moon]]''. He used many techniques – one of which was to stop the camera rolling, change something in the scene, and then continue rolling the film. This is a very similar idea to that of what later became [[stop motion|stop-motion]] animation. Méliès accidentally happened upon the technique when his camera broke down while shooting a bus driving by. When the camera was fixed, a horse happened to be passing by just as Méliès continued to film. The result was that the bus appeared to change into a horse. |
|||
[[J. Stuart Blackton]] was possibly the first American filmmaker to use the techniques of stop-motion and hand-drawn animation. Introduced to filmmaking by [[Edison]], he pioneered these concepts at the turn of the 20th century, with his first copyrighted work dated 1900. Several of his films, among them ''[[The Enchanted Drawing]]'' (1900) and ''[[Humorous Phases of Funny Faces]]'' (1906) were film versions of Blackton's "lightning artist" routine, and utilized modified versions of Méliès' early stop-motion techniques to make a series of [[blackboard]] drawings appear to move and reshape themselves. ''Humorous Phases of Funny Faces' is regularly cited as the first true animated film, and Blackton is considered the first true [[animator]]. |
|||
Another French artist, [[Émile Cohl]], began drawing cartoon strips and created a film in 1908 called ''Fantasmagorie''. The film largely consisted of a [[stick figure]] moving about and encountering all manner of morphing objects, such as a wine bottle that transforms into a flower. There were also sections of live action where the animator’s hands would enter the scene. The film was created by drawing each frame on paper and then shooting each frame onto [[negative film]], which gave the picture a blackboard look. This makes ''Fantasmagorie'' the first animated film created using what came to be known as [[traditional animation|traditional (hand-drawn) animation]]. |
|||
Following the successes of Blackton and Cohl, many other artists began experimenting with animation. One such artist was [[Winsor McCay]], a successful newspaper cartoonist, who created detailed animations that required a team of artists and painstaking attention for detail. Each frame was drawn on paper; which invariably required backgrounds and characters to be redrawn and animated. Among McCay's most noted films are ''[[Little Nemo]]'' (1911), ''[[Gertie the Dinosaur]]'' (1914) and ''[[The Sinking of the Lusitania]]'' (1918). |
|||
The production of animated short films, typically referred to as "cartoons", became an industry of its own during the 1910s, and cartoon shorts were produced to be shown in [[movie theaters]]. The most successful early animation producer was [[John Randolph Bray]], who, along with [[animator]] [[Earl Hurd]], patented the [[cel animation]] process which dominated the animation industry for the rest of the decade. |
|||
==Techniques== |
|||
===Traditional animation=== |
|||
[[Image:Animhorse.gif|right|thumb|200px|An example of traditional animation, a horse animated by [[rotoscoping]] from [[Edweard Muybridge|Edward Muybridge's]] 19th century photos.]] |
|||
{{Main|Traditional animation}} |
|||
(Also called [[cel animation]]) Traditional animation was the process used for most animated films of the 20th century. The individual frames of a traditionally animated film are photographs of drawings, which are first drawn on paper. To create the illusion of movement, each drawing differs slightly from the one before it. The animators' drawings are traced or photocopied onto transparent acetate sheets called [[cel]]s, which are filled in with paints in assigned colors or tones on the side opposite the line drawings. The completed character cels are photographed one-by-one onto motion picture film against a painted background by a [[rostrum camera]]. |
|||
The traditional cel animation process became obsolete by the beginning of the 21st century. Today, animators' drawings and the backgrounds are either scanned into or drawn directly into a computer system. Various [[software]] programs are used to color the drawings and simulate camera movement and effects. The final animated piece is output to one of several delivery mediums, including traditional [[35 mm film]] and newer media such as [[digital video]]. The "look" of traditional cel animation is still preserved, and the [[character animator]]s' work has remained essentially the same over the past 70 years. Some animation producers have used the term "tradigital" to describe cel animation which makes extensive use of computer technology. |
|||
Examples of traditionally animated feature films include ''[[Pinocchio (1940 film)|Pinocchio]]'' ([[United States]], 1940), ''[[Animal Farm (1954 film)|Animal Farm]]'' ([[United Kingdom]], 1954), and ''[[Akira (film)|Akira]]'' ([[Japan]], 1988). Traditional animated films which were produced with the aid of computer technology include ''[[The Lion King]]'' (US, 1994) ''[[Spirited Away|Sen to Chihiro no Kamikakushi (Spirited Away)]]'' (Japan, 2001), and ''[[Les Triplettes de Belleville]]'' (2003). |
|||
*'''Full animation''' refers to the process of producing high-quality traditionally animated films, which regularly use detailed drawings and plausible movement. Fully animated films can be done in a variety of styles, from realistically designed works such as those produced by the [[Walt Disney Animation Studios|Walt Disney studio]], to the more "cartoony" styles of those produced by the [[Warner Bros. Cartoons|Warner Bros. animation studio]]. Many of the [[Disney animated features]] are examples of full animation, as are non-Disney works such as ''[[An American Tail]]'' (US, 1986) and ''[[The Iron Giant]]'' (US, 1999) |
|||
*'''[[Limited animation]]''' involves the use of less detailed and/or more stylized drawings and methods of movement. Pioneered by the artists at the American studio [[United Productions of America]], limited animation can be used as a method of stylized artistic expression, as in ''[[Gerald McBoing Boing]]'' (US, 1951), ''[[Yellow Submarine (film)|Yellow Submarine]]'' (UK, 1968), and much of the [[anime]] produced in Japan. Its primary use, however, has been in producing cost-effective animated content for media such as [[television]] (the work of [[Hanna-Barbera]], [[Filmation]], and other TV animation studios) and later [[the Internet]] ([[web cartoon]]s). |
|||
*'''[[Rotoscope|Rotoscoping]]''' is a technique, patented by [[Max Fleischer]] in 1917, where animators trace live-action movement, [[frame (film)|frame]] by frame. The source film can be directly copyed from actors' outlines into animated drawings, as in ''[[The Lord of the Rings (1978 film)|The Lord of the Rings]]'' (US, 1978), used as a basis and inspiration for character animation, as in most Disney films, or used in a stylized and expressive manner, as in ''[[Waking Life]]'' (US, 2001) and ''[[A Scanner Darkly (film)]]'' (US, 2006). |
|||
* '''Stop-motion Animation''', used to describe animation created by physically manipulating real-world objects and photographing them one frame of film at a time to create the illusion of movement. There are many different types of stop-motion animation, usually named after the type of media used to create the animation. |
|||
[[Image:Claychick.jpg|thumb|200px|A clay animation scene from a TV commercial.]] |
|||
*'''[[Clay animation]]''', often abbreviated as ''claymation'', uses figures made of clay or a similar malleable material to create stop-motion animation. The figures may have an [[armature]] or wire frame inside of them, similar to the related puppet animation (below), that can be manipulated in order to pose the figures. Alternatively, the figures may be made entirely of clay, such as in the films of [[Bruce Bickford]], where clay creatures morph into a variety of different shapes. Examples of clay-animated works include ''[[The Gumby Show]]'' (US, 1957-1967) ''[[Morph (character)|Morph]]'' shorts (UK, 1977-2000), ''[[Wallace and Gromit]]'' shorts (UK, 1989-1995 and 2000 - ?), [[Jan Švankmajer]]'s ''Dimensions of Dialogue'' ([[Czechoslovakia]], 1982), ''[[The Amazing Mr. Bickford]]'' (US, 1987), and ''[[The Trap Door]]'' (UK, 1984). |
|||
*'''[[Cutout animation]]''' is a type of stop-motion animation produced by moving 2-dimensional pieces of material such as paper or cloth. Examples include [[Terry Gilliam]]'s animated sequences from ''[[Monty Python's Flying Circus]]'' (UK, 1969-1974); ''[[Fantastic Planet|La Planète sauvage (Fantastic Planet)]]'' (France/Czechoslovakia, 1973) ; ''[[Tale of Tales|Skazka skazok (Tale of Tales)]]'' ([[Russia]], 1979), and the pilot episode of the TV series ''[[South Park]]'' (US, 1997). |
|||
**'''[[Silhouette animation]]''' is a monochrome variant of cutout animation in which the characters are only visible as black silhouettes. Examples include ''[[The Adventures of Prince Achmed]]'' ([[Weimar Republic]], 1926) and ''[[Princes et princesses]]'' (France, 2000). |
|||
*'''[[Graphic animation]]''' uses non-drawn flat visual graphic material (photographs, newspaper clippings, magazines, etc.) which are sometimes manipulated frame-by-frame to create movement. At other times, the graphics remain stationary, while the stop-motion camera is moved to create on-screen action. |
|||
*'''[[Model animation]]''' refers to stop-motion animation created to interact with and exist as a part of a live-action world. Intercutting, [[matte]] effects, and split screens are often employed to blend stop-motion characters or objects with live actors and settings. Examples include the work of [[Ray Harryhausen]], as seen in films such ''[[Jason and the Argonauts (film)|Jason and the Argonauts]]'' (1961), and the work of [[Willis O'Brien]] on films such as ''[[King Kong (1933 film)|King Kong]]'' (1933 film). |
|||
**'''[[Go motion]]''' is a variant of model animation which uses various techniques to create [[motion blur]] between frames of film, which is not present in traditional stop-motion. The technique was invented by [[Industrial Light and Magic]] and [[Phil Tippett]] to create [[special effects]] scenes for the film ''[[The Empire Strikes Back]]'' (1980). |
|||
*'''[[Object animation]]''' refers to the use of regular inanimate objects in stop-motion animation, as opposed to specially created items. One example of object animation is the '''[[Brickfilming|brickfilm]]''', which incorporates the use of plastic toy construction blocks such as [[LEGO]]s. |
|||
*'''[[Pixilation]]''' involves the use of live humans as stop motion characters. This allows for a number of surreal effects, including disappearances and reappearances, allowing people to appear to slide across the ground, and other such effects. Examples of pixilation include [[Norman McLaren]]'s ''[[Neighbours (film)|Neighbours]]'' ([[Canada]], 1952). |
|||
*'''[[Puppet animation]]''' typically involves stop-motion puppet figures interacting with each other in a constructed environment, in contrast to the real-world interaction in model animation. The puppets generally have an [[armature]] inside of them to keep them still and steady as well as constraining them to move at particular joints. Examples include ''[[The Tale of the Fox| Le Roman de Renard (The Tale of the Fox)]]'' (France, 1937), the films of [[Jiří Trnka]], ''[[The Nightmare Before Christmas]]'' (US, 1993), and the TV series ''[[Robot Chicken]]'' (US, 2005-present). |
|||
**'''[[Puppetoon]]''', created using techniques developed by [[George Pál]], are puppet-animated films which typically use a different version of a puppet for different frames, rather than simply manipulating one existing puppet. |
|||
===Computer animation=== |
|||
[[Image:Rotating earth (large).gif|thumb|150px| A short [[gif]] animation]] |
|||
{{Main|Computer animation}} |
|||
Like stop motion, computer animation encompasses a variety of techniques, the unifying idea being that the animation is created digitally on a computer. |
|||
:'''2D animation''' |
|||
:Figures are created and/or edited on the computer using 2D [[bitmap graphics]] or created and edited using 2D [[vector graphics]]. This includes automated computerized versions of traditional animation techniques such as of [[tweening]], [[morphing]], [[onion skinning]] and [[interpolated]] rotoscoping. |
|||
:Examples: ''[[Foster's Home for Imaginary Friends]]'', ''[[Jib Jab]]'', ''[[Mickey the Squirrel]]'' |
|||
:*Analog computer animation |
|||
:*[[Flash animation]] |
|||
:*[[PowerPoint animation]] |
|||
<!-- Commented out because image was deleted: [[Image:Duck3D.jpg|thumb|150px|An animated duck.]] --> |
|||
:'''[[3D animation]]''' |
|||
:Digital models manipulated by an animator. In order to manipulate a mesh, it is given a digital [[armature (sculpture)]]. This process is called rigging. Various other techniques can be applied, such as mathematical functions (ex. gravity, particle simulations), simulated fur or hair, effects such as fire and water and the use of [[Motion capture]] to name but a few. Many [[3D computer graphics|3D]] [[animations]] are very believable and are commonly used as [[special effects]] for recent movies.<br> |
|||
:Examples: ''[[The Incredibles]]'', ''[[Shrek]]'', ''[[Finding Nemo]]'', ''[[Flatland]]'' |
|||
:'''3D animation Terms''' |
|||
:*[[Cel-shaded animation]] |
|||
:*[[Morph target animation]] |
|||
:*[[Skeletal animation]] |
|||
:*[[Motion capture]] |
|||
:*[[Crowd simulation]] |
|||
........ |
|||
===Experimental animation techniques=== |
|||
*'''[[Drawn on film animation]]''': a technique where footage is produced by creating the images directly on [[film stock]], for example by [[Norman McLaren]] and [[Len Lye]]. |
|||
*'''[[Paint-on-glass animation]]''': a technique for making animated films by manipulating slow drying [[oil paint]]s on sheets of [[glass]]. |
|||
*'''[[Pinscreen animation]]''': makes use of a screen filled with movable pins, which can be moved in or out by pressing an object onto the screen. The screen is lit from the side so that the pins cast shadows. The technique has been used to create animated films with a range of textural effects difficult to achieve with traditional cel animation. |
|||
*'''[[Sand animation]]''': sand is moved around on a backlighted or frontlighted piece of glass to create each frame for an animated film. This creates an interesting effect when animated because of the [[light]] [[contrast]]. |
|||
===Other techniques and approaches=== |
|||
*[[Character animation]] |
|||
*[[Chuckimation]] |
|||
*[[Multi-sketch]]ing |
|||
*[[Special effects animation]] |
|||
==See also== |
|||
{{Wiktionarypar|animation}} |
|||
{{wikinews|Annie Awards for animation Sunday; Wikinews will be there}} |
|||
* [[Animation software]] |
|||
* [[Art]] |
|||
* [[Avar (animation variable)]] |
|||
* [[Computer generated imagery]] |
|||
* [[Film genre|List of movie genres]] |
|||
* [[International Tournée of Animation]] |
|||
* [[List of animated shorts]] |
|||
* [[List of animation studios]] |
|||
* [[List of film-related topics|List of motion picture topics]] |
|||
* [[Motion graphic design]] |
|||
* [[Slideshow animation]] |
|||
* [[Stick figure]] |
|||
* [[Wire frame model]] |
|||
==References== |
|||
{{Nofootnotes|date=February 2008}} |
|||
{{reflist}} |
|||
*Ball, R., Beck, J., DeMott R., Deneroff, H., Gerstein, D., Gladstone, F., Knott, T., Leal, A., Maestri, G., Mallory, M., Mayerson, M., McCracken, H., McGuire, D., Nagel, J., Pattern, F., Pointer, R., Webb, P., Robinson, C., Ryan, W., Scott, K., Snyder, A. & Webb, G. (2004) ''Animation Art: From Pencil to Pixel, the History of Cartoon, Anime & CGI''. Fulhamm London.: Flame Tree Publishing. ISBN 1-84451-140-5 |
|||
*Crafton, Donald (1982). ''Before Mickey''. Cambridge, Massachusetts.: The MIT Press. ISBN 0-262-03083-7 |
|||
*Solomon, Charles (1989). ''Enchanted Drawings: The History of Animation''. New York.: Random House, Inc. ISBN 0-394-54684-9 |
|||
==Further reading== |
|||
*[http://www.uca.edu/org/ccsmi/ccsmi/classicwork/Myth%20Revisited.htm Anderson, Joseph and Barbara, "The Myth of Persistence of Vision Revisited", ''Journal of Film and Video''], Vol. 45, No. 1 (Spring 1993): 3-12 |
|||
*Culhane, Shamus, ''Animation Script to Screen'' |
|||
*Laybourne, Kit, ''The Animation Book'' |
|||
*Ledoux, Trish, Ranney, Doug, & Patten, Fred (Ed.), ''Complete Anime Guide: Japanese Animation Film Directory and Resource Guide'', Tiger Mountain Press 1997 |
|||
*Masson, Terrence, [http://www.cg101.com ''CG101: A Computer Graphics Industry Reference''] Unique and personal histories of early computer animation production, plus a comprehensive foundation of the industry for all reading levels. ISBN 0-9778710-0-2 |
|||
*[[Frank Thomas (animator)|Thomas, Frank]] and [[Ollie Johnston|Johnston, Ollie]], ''[[The Illusion Of Life|Disney Animation: The Illusion Of Life]]'', Abbeville 1981 |
|||
*Walters, Faber and Helen (Ed.), ''Animation Unlimited: Innovative Short Films Since 1940'', HarperCollins Publishers, 2004 |
|||
*[[Richard Williams|Williams, Richard]], ''[[The Animator's Survival Kit]]'' ISBN 0-5712-0228-4 |
|||
* Bob Godfrey and Anna Jackson, 'The Do-It-Yourself Film Animation Book' BBC Publications 1974 ISBN 0-563-10829-0 Now out of print but available s/hand through a range of sources such as Amazon Uk. |
|||
==External links== |
|||
{{Commonscat|Animation}} |
|||
* {{dmoz|Arts/Animation/}} |
|||
* [http://www.animation.randomboo.com/ Everything Animation. The Animation ScrapBook] |
|||
* [http://anm.sagepub.com Animation: An Interdisciplinary Journal] |
|||
* [http://academic.evergreen.edu/curricular/eat/handouts/Pictures/CutSandPaintRules.pdf Experimental Animation Techniques] |
|||
* [http://www.animated-divots.com/chronst.html Chronology of Animation] |
|||
* [http://www.sci.fi/~animato/cartoon/cartoon.html How An Animated Cartoon is Made] |
|||
* [http://www.animationarena.com/principles-of-animation.html 28 Principles of Animation] |
|||
* [http://www.nfb.ca/animation/objanim/en/ ''Focus on Animation''] - A National Film Board of Canada Web site that explains animation techniques discussed in this article and presents viewable animation classics as examples. |
|||
* [http://www.nfb.ca/animation/objanim/en/films/film.php?sort=director&director=Magalh%E3es%2C+Marcos&id=16804 "Animando"], a 12-minute film demonstrating 10 different animation techniques (and teaching how to use them). |
|||
* [http://www.aniboom.com Aniboom animation] online animation festival. |
|||
* [http://rodmena.com/iquence Advanced Digital Animation Sequence Managing System.] |
|||
* [http://www.ucreative.ac.uk/index.cfm?articleid=11263 Animation Research Centre] |
|||
{{Animation}} |
|||
{{DEFAULTSORT: }} |
|||
[[Category:Animation]] |
|||
[[Category:Film and video technology]] |
|||
[[Category:Stop motion]] |
|||
[[ar:رسوم متحركة]] |
|||
[[bs:Animacija]] |
|||
[[bg:Анимация]] |
|||
[[ca:Animació]] |
|||
[[cs:Animace]] |
|||
[[da:Animation]] |
|||
[[de:Animation]] |
|||
[[et:Animatsioon]] |
|||
[[es:Animación]] |
|||
[[fa:پویانمایی]] |
|||
[[fr:Animation]] |
|||
[[ko:애니메이션]] |
|||
[[id:Animasi]] |
|||
[[is:Teiknimynd]] |
|||
[[it:Animazione]] |
|||
[[he:אנימציה]] |
|||
[[ka:ანიმაცია]] |
|||
[[lv:Multiplikācija]] |
|||
[[mk:Анимација]] |
|||
[[ms:Animasi]] |
|||
[[nl:Animatie]] |
|||
[[ja:アニメーション]] |
|||
[[no:Animasjon]] |
|||
[[pl:Animacja]] |
|||
[[pt:Animação]] |
|||
[[ro:Animaţie]] |
|||
[[ru:Мультипликация]] |
|||
[[sq:Animimi]] |
|||
[[simple:Animation]] |
|||
[[sl:Animacija]] |
|||
[[sr:Анимација]] |
|||
[[fi:Animaatio]] |
|||
[[sv:Animering]] |
|||
[[ta:இயங்குபடம்]] |
|||
[[th:แอนิเมชัน]] |
|||
[[tr:Animasyon]] |
|||
[[uk:Анімація]] |
|||
[[bat-smg:Moltėplėkacėjė]] |
|||
[[zh:动画]] |
|||
Revision as of 19:15, 20 March 2008

The bouncing ball animation (below) consists of these 6 frames.
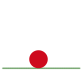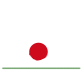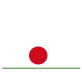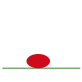
This animation moves at 10 frames per second.
Animation is the rapid display of a sequence of images of 2-D artwork or model positions in order to create an illusion of movement. It is an optical illusion of motion due to the phenomenon of persistence of vision, and can be created and demonstrated in a number of ways. The most common method of presenting animation is as a motion picture or video program, although several other forms of presenting animation also exist.
Animation can sometimes refer to a way of activating a community, i.e. 'animating' the users. This means actions which encourages users to interact with a given service and is connected to moderation.
History
Early examples of attempts to capture the phenomenon of motion into a still drawing can be found in paleolithic cave paintings, where animals are depicted with multiple legs in superimposed positions, clearly attempting to convey the perception of motion.
The phenakistoscope, zoetrope and praxinoscope, as well as the common flip book, were early popular animation devices invented during the 1800s. These devices produced movement from sequential drawings using technological means, but animation did not really develop much further until the advent of motion picture film.
There is no single person who can be considered the "creator" of the art of film animation, as there were several people doing several projects which could be considered various types of animation all around the same time.
French filmmaker Georges Méliès was a creator of special effect films, such as A Trip to the Moon. He used many techniques – one of which was to stop the camera rolling, change something in the scene, and then continue rolling the film. This is a very similar idea to that of what later became stop-motion animation. Méliès accidentally happened upon the technique when his camera broke down while shooting a bus driving by. When the camera was fixed, a horse happened to be passing by just as Méliès continued to film. The result was that the bus appeared to change into a horse.
J. Stuart Blackton was possibly the first American filmmaker to use the techniques of stop-motion and hand-drawn animation. Introduced to filmmaking by Edison, he pioneered these concepts at the turn of the 20th century, with his first copyrighted work dated 1900. Several of his films, among them The Enchanted Drawing (1900) and Humorous Phases of Funny Faces (1906) were film versions of Blackton's "lightning artist" routine, and utilized modified versions of Méliès' early stop-motion techniques to make a series of blackboard drawings appear to move and reshape themselves. Humorous Phases of Funny Faces' is regularly cited as the first true animated film, and Blackton is considered the first true animator.
Another French artist, Émile Cohl, began drawing cartoon strips and created a film in 1908 called Fantasmagorie. The film largely consisted of a stick figure moving about and encountering all manner of morphing objects, such as a wine bottle that transforms into a flower. There were also sections of live action where the animator’s hands would enter the scene. The film was created by drawing each frame on paper and then shooting each frame onto negative film, which gave the picture a blackboard look. This makes Fantasmagorie the first animated film created using what came to be known as traditional (hand-drawn) animation.
Following the successes of Blackton and Cohl, many other artists began experimenting with animation. One such artist was Winsor McCay, a successful newspaper cartoonist, who created detailed animations that required a team of artists and painstaking attention for detail. Each frame was drawn on paper; which invariably required backgrounds and characters to be redrawn and animated. Among McCay's most noted films are Little Nemo (1911), Gertie the Dinosaur (1914) and The Sinking of the Lusitania (1918).
The production of animated short films, typically referred to as "cartoons", became an industry of its own during the 1910s, and cartoon shorts were produced to be shown in movie theaters. The most successful early animation producer was John Randolph Bray, who, along with animator Earl Hurd, patented the cel animation process which dominated the animation industry for the rest of the decade.
Techniques
Traditional animation

(Also called cel animation) Traditional animation was the process used for most animated films of the 20th century. The individual frames of a traditionally animated film are photographs of drawings, which are first drawn on paper. To create the illusion of movement, each drawing differs slightly from the one before it. The animators' drawings are traced or photocopied onto transparent acetate sheets called cels, which are filled in with paints in assigned colors or tones on the side opposite the line drawings. The completed character cels are photographed one-by-one onto motion picture film against a painted background by a rostrum camera.
The traditional cel animation process became obsolete by the beginning of the 21st century. Today, animators' drawings and the backgrounds are either scanned into or drawn directly into a computer system. Various software programs are used to color the drawings and simulate camera movement and effects. The final animated piece is output to one of several delivery mediums, including traditional 35 mm film and newer media such as digital video. The "look" of traditional cel animation is still preserved, and the character animators' work has remained essentially the same over the past 70 years. Some animation producers have used the term "tradigital" to describe cel animation which makes extensive use of computer technology.
Examples of traditionally animated feature films include Pinocchio (United States, 1940), Animal Farm (United Kingdom, 1954), and Akira (Japan, 1988). Traditional animated films which were produced with the aid of computer technology include The Lion King (US, 1994) Sen to Chihiro no Kamikakushi (Spirited Away) (Japan, 2001), and Les Triplettes de Belleville (2003).
- Full animation refers to the process of producing high-quality traditionally animated films, which regularly use detailed drawings and plausible movement. Fully animated films can be done in a variety of styles, from realistically designed works such as those produced by the Walt Disney studio, to the more "cartoony" styles of those produced by the Warner Bros. animation studio. Many of the Disney animated features are examples of full animation, as are non-Disney works such as An American Tail (US, 1986) and The Iron Giant (US, 1999)
- Limited animation involves the use of less detailed and/or more stylized drawings and methods of movement. Pioneered by the artists at the American studio United Productions of America, limited animation can be used as a method of stylized artistic expression, as in Gerald McBoing Boing (US, 1951), Yellow Submarine (UK, 1968), and much of the anime produced in Japan. Its primary use, however, has been in producing cost-effective animated content for media such as television (the work of Hanna-Barbera, Filmation, and other TV animation studios) and later the Internet (web cartoons).
- Rotoscoping is a technique, patented by Max Fleischer in 1917, where animators trace live-action movement, frame by frame. The source film can be directly copyed from actors' outlines into animated drawings, as in The Lord of the Rings (US, 1978), used as a basis and inspiration for character animation, as in most Disney films, or used in a stylized and expressive manner, as in Waking Life (US, 2001) and A Scanner Darkly (film) (US, 2006).
- Stop-motion Animation, used to describe animation created by physically manipulating real-world objects and photographing them one frame of film at a time to create the illusion of movement. There are many different types of stop-motion animation, usually named after the type of media used to create the animation.

- Clay animation, often abbreviated as claymation, uses figures made of clay or a similar malleable material to create stop-motion animation. The figures may have an armature or wire frame inside of them, similar to the related puppet animation (below), that can be manipulated in order to pose the figures. Alternatively, the figures may be made entirely of clay, such as in the films of Bruce Bickford, where clay creatures morph into a variety of different shapes. Examples of clay-animated works include The Gumby Show (US, 1957-1967) Morph shorts (UK, 1977-2000), Wallace and Gromit shorts (UK, 1989-1995 and 2000 - ?), Jan Švankmajer's Dimensions of Dialogue (Czechoslovakia, 1982), The Amazing Mr. Bickford (US, 1987), and The Trap Door (UK, 1984).
- Cutout animation is a type of stop-motion animation produced by moving 2-dimensional pieces of material such as paper or cloth. Examples include Terry Gilliam's animated sequences from Monty Python's Flying Circus (UK, 1969-1974); La Planète sauvage (Fantastic Planet) (France/Czechoslovakia, 1973) ; Skazka skazok (Tale of Tales) (Russia, 1979), and the pilot episode of the TV series South Park (US, 1997).
- Silhouette animation is a monochrome variant of cutout animation in which the characters are only visible as black silhouettes. Examples include The Adventures of Prince Achmed (Weimar Republic, 1926) and Princes et princesses (France, 2000).
- Graphic animation uses non-drawn flat visual graphic material (photographs, newspaper clippings, magazines, etc.) which are sometimes manipulated frame-by-frame to create movement. At other times, the graphics remain stationary, while the stop-motion camera is moved to create on-screen action.
- Model animation refers to stop-motion animation created to interact with and exist as a part of a live-action world. Intercutting, matte effects, and split screens are often employed to blend stop-motion characters or objects with live actors and settings. Examples include the work of Ray Harryhausen, as seen in films such Jason and the Argonauts (1961), and the work of Willis O'Brien on films such as King Kong (1933 film).
- Go motion is a variant of model animation which uses various techniques to create motion blur between frames of film, which is not present in traditional stop-motion. The technique was invented by Industrial Light and Magic and Phil Tippett to create special effects scenes for the film The Empire Strikes Back (1980).
- Object animation refers to the use of regular inanimate objects in stop-motion animation, as opposed to specially created items. One example of object animation is the brickfilm, which incorporates the use of plastic toy construction blocks such as LEGOs.
- Pixilation involves the use of live humans as stop motion characters. This allows for a number of surreal effects, including disappearances and reappearances, allowing people to appear to slide across the ground, and other such effects. Examples of pixilation include Norman McLaren's Neighbours (Canada, 1952).
- Puppet animation typically involves stop-motion puppet figures interacting with each other in a constructed environment, in contrast to the real-world interaction in model animation. The puppets generally have an armature inside of them to keep them still and steady as well as constraining them to move at particular joints. Examples include Le Roman de Renard (The Tale of the Fox) (France, 1937), the films of Jiří Trnka, The Nightmare Before Christmas (US, 1993), and the TV series Robot Chicken (US, 2005-present).
- Puppetoon, created using techniques developed by George Pál, are puppet-animated films which typically use a different version of a puppet for different frames, rather than simply manipulating one existing puppet.
Computer animation

Like stop motion, computer animation encompasses a variety of techniques, the unifying idea being that the animation is created digitally on a computer.
- 2D animation
- Figures are created and/or edited on the computer using 2D bitmap graphics or created and edited using 2D vector graphics. This includes automated computerized versions of traditional animation techniques such as of tweening, morphing, onion skinning and interpolated rotoscoping.
- Examples: Foster's Home for Imaginary Friends, Jib Jab, Mickey the Squirrel
- Analog computer animation
- Flash animation
- PowerPoint animation
- 3D animation
- Digital models manipulated by an animator. In order to manipulate a mesh, it is given a digital armature (sculpture). This process is called rigging. Various other techniques can be applied, such as mathematical functions (ex. gravity, particle simulations), simulated fur or hair, effects such as fire and water and the use of Motion capture to name but a few. Many 3D animations are very believable and are commonly used as special effects for recent movies.
- Examples: The Incredibles, Shrek, Finding Nemo, Flatland
- 3D animation Terms
........
Experimental animation techniques
- Drawn on film animation: a technique where footage is produced by creating the images directly on film stock, for example by Norman McLaren and Len Lye.
- Paint-on-glass animation: a technique for making animated films by manipulating slow drying oil paints on sheets of glass.
- Pinscreen animation: makes use of a screen filled with movable pins, which can be moved in or out by pressing an object onto the screen. The screen is lit from the side so that the pins cast shadows. The technique has been used to create animated films with a range of textural effects difficult to achieve with traditional cel animation.
- Sand animation: sand is moved around on a backlighted or frontlighted piece of glass to create each frame for an animated film. This creates an interesting effect when animated because of the light contrast.
Other techniques and approaches
See also
- Animation software
- Art
- Avar (animation variable)
- Computer generated imagery
- List of movie genres
- International Tournée of Animation
- List of animated shorts
- List of animation studios
- List of motion picture topics
- Motion graphic design
- Slideshow animation
- Stick figure
- Wire frame model
References
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (February 2008) |
- Ball, R., Beck, J., DeMott R., Deneroff, H., Gerstein, D., Gladstone, F., Knott, T., Leal, A., Maestri, G., Mallory, M., Mayerson, M., McCracken, H., McGuire, D., Nagel, J., Pattern, F., Pointer, R., Webb, P., Robinson, C., Ryan, W., Scott, K., Snyder, A. & Webb, G. (2004) Animation Art: From Pencil to Pixel, the History of Cartoon, Anime & CGI. Fulhamm London.: Flame Tree Publishing. ISBN 1-84451-140-5
- Crafton, Donald (1982). Before Mickey. Cambridge, Massachusetts.: The MIT Press. ISBN 0-262-03083-7
- Solomon, Charles (1989). Enchanted Drawings: The History of Animation. New York.: Random House, Inc. ISBN 0-394-54684-9
Further reading
- Anderson, Joseph and Barbara, "The Myth of Persistence of Vision Revisited", Journal of Film and Video, Vol. 45, No. 1 (Spring 1993): 3-12
- Culhane, Shamus, Animation Script to Screen
- Laybourne, Kit, The Animation Book
- Ledoux, Trish, Ranney, Doug, & Patten, Fred (Ed.), Complete Anime Guide: Japanese Animation Film Directory and Resource Guide, Tiger Mountain Press 1997
- Masson, Terrence, CG101: A Computer Graphics Industry Reference Unique and personal histories of early computer animation production, plus a comprehensive foundation of the industry for all reading levels. ISBN 0-9778710-0-2
- Thomas, Frank and Johnston, Ollie, Disney Animation: The Illusion Of Life, Abbeville 1981
- Walters, Faber and Helen (Ed.), Animation Unlimited: Innovative Short Films Since 1940, HarperCollins Publishers, 2004
- Williams, Richard, The Animator's Survival Kit ISBN 0-5712-0228-4
- Bob Godfrey and Anna Jackson, 'The Do-It-Yourself Film Animation Book' BBC Publications 1974 ISBN 0-563-10829-0 Now out of print but available s/hand through a range of sources such as Amazon Uk.
External links
- Animation at Curlie
- Everything Animation. The Animation ScrapBook
- Animation: An Interdisciplinary Journal
- Experimental Animation Techniques
- Chronology of Animation
- How An Animated Cartoon is Made
- 28 Principles of Animation
- Focus on Animation - A National Film Board of Canada Web site that explains animation techniques discussed in this article and presents viewable animation classics as examples.
- "Animando", a 12-minute film demonstrating 10 different animation techniques (and teaching how to use them).
- Aniboom animation online animation festival.
- Advanced Digital Animation Sequence Managing System.
- Animation Research Centre
