2,2-dimethylpentane
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 2,2-dimethylpentane | |||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 16 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
highly flammable colorless liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 100.21 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.67 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−123 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
79 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
111 mbar (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.3822 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
2,2-Dimethylpentane is a chemical compound from the group of aliphatic saturated hydrocarbons . It is one of the nine constitutional isomers of heptane .
Extraction and presentation
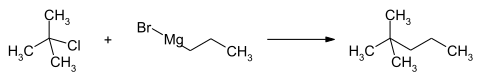
2,2-Dimethylpentane can be obtained by the isomerization of n -heptane , where the compound has to be separated from the resulting mixture of isomers. A laboratory synthesis takes place via the conversion of the Grignard compound from n -propyl bromide with tert-butyl chloride .
properties
Physical Properties
2,2-Dimethylpentane is a highly flammable and colorless liquid. The vapor pressure function results according to Antoine according to log 10 (P) = A− (B / (T + C)) (P in bar, T in K) with A = 3.93999, B = 1190.298 and C = −49.807 in the temperature range from 288 to 353 K.
The most important thermodynamic properties are listed in the following table:
| property | Type | value |
|---|---|---|
| Standard enthalpy of formation | Δ f H 0 gas Δ f H 0 liquid |
−206.2 kJ mol −1 −238.7 kJ mol −1 |
| Enthalpy of combustion | Δ c H 0 liquid | −4802.6 kJ mol −1 |
| Heat capacity | c p | 221.12 J mol −1 K −1 (25 ° C) as a liquid |
| Enthalpy of fusion | Δ f H 0 | 5.824 kJ mol −1 at the melting point |
| Entropy of fusion | Δ f S 0 | 38.98 kJ mol −1 at the melting point |
| Enthalpy of evaporation | Δ V H 0 | 29.23 kJ mol −1 at the normal pressure boiling point 32.56 kJ mol −1 at 25 ° C |
| Critical temperature | T C | 247.4 ° C |
| Critical pressure | P C | 27.7 bar |
| Critical volume | V C | 0.416 l mol −1 |
| Critical density | ρ C | 2.41 mol·l −1 |
Safety-related parameters
2,2-Dimethylpentane forms highly flammable vapor-air mixtures. The compound has a flash point of −21 ° C. The explosion range is between 0.9% by volume (40 g / m 3 ) as the lower explosion limit (LEL) and 6.9% by volume (285 g / m 3 ) as the upper explosion limit (UEL). The ignition temperature is 320 ° C. The substance therefore falls into temperature class T3.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j Entry on 2,2-dimethylpentane in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 88th edition. (Internet version: 2008), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-206.
- ↑ Patent application US2004059174A1 : C7 + paraffin isomerization process and catalyst therefore. Published on 2004 , Inventors: J. Houzvicka, NJ Blom.
- ↑ Patent application US2004249231A1 : Isomerization catalyst and processes. Published on 2004 , Inventor: Gillespie, RD.
- ↑ Patent application US2007123745A1 : Process for the preparation of a paraffin isomerization catalys. Published on 2007 , Inventors: K. Herbst, P. Stern, NJ Blom, G. Starch-Hytoft, KG Knudsen.
- ↑ Russell E. Marker, Thomas S. Oakwood: Hexamethylethane and Tetraalkylmethanes . In: Journal of the American Chemical Society . tape 60 , no. November 11 , 1938, pp. 2598-2598 , doi : 10.1021 / ja01278a011 .
- ↑ a b c d e Thomas E. Daubert: Vapor-Liquid Critical Properties of Elements and Compounds. 5. Branched Alkanes and Cycloalkanes . In: Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data . tape 41 , no. 3 , May 1996, pp. 365-372 , doi : 10.1021 / je9501548 .
- ↑ a b c E. J. Rossini, FD Prosen: Heats of combustion and formation of the paraffinic hydrocarbons at 25 C . In: The Journal of Research of the National Institute of Standards and Technology . Vol. 34, No. 3 , 1945, p. 263-267 ( facsimile ).
- ↑ a b c H. M. Huffman, ME Gross, DW Scott, JP McCullough: Low temperature thermodynamic properties of six isomeric heptanes . In: The Journal of Physical Chemistry . tape 65 , no. 3 , March 1961, p. 495-503 , doi : 10.1021 / j100821a026 .
- ^ A b V. Majer, V. Svoboda: Enthalpies of Vaporization of Organic Compounds: A Critical Review and Data Compilation . Blackwell Scientific, Oxford 1985, p. 300.
- ↑ a b E. Brandes, W. Möller: Safety-related parameters - Volume 1: Flammable liquids and gases . Wirtschaftsverlag NW - Verlag für neue Wissenschaft, Bremerhaven 2003.