2-chloro-2-methylpropane
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 2-chloro-2-methylpropane | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
tert -butyl chloride |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 4 H 9 Cl | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 92.57 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.84 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−27.1 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
51 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
|
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
sparingly soluble in water (2.9 g l −1 at 15 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.3857 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
2-chloro-2-methylpropane ( tert-butyl chloride) is a colorless, water-clear liquid. It belongs to the group of haloalkanes and is the simplest tertiary chloroalkane.
Manufacturing
The synthesis of 2-chloro-2-methylpropane succeeds in very good yield by nucleophilic substitution (reaction type S N 1) of tert-butyl alcohol with concentrated hydrochloric acid ( Lucas reaction ). The product is purified by drying and subsequent distillation .
As a by-product of this reaction, 2-methylpropene ( isobutene ) is formed by splitting off a proton from the intermediate carbenium ion . Industrial production can take place as a gas phase reaction between isobutene and hydrogen chloride in the presence of aluminum oxide at 100.degree.
properties
Physical Properties
2-chloro-2-methylpropane is a colorless, easily mobile liquid. At 0.842 g / cm 3, it has a lower density than water. It is quite volatile and already boils at around 51 ° C. It is miscible in all proportions with most organic solvents.
Chemical properties
As a tertiary haloalkane, 2-chloro-2-methylpropane reacts rather slowly compared to other haloalkanes due to the steric hindrance. S N 2 reactions are hardly possible. In the reaction with bases with elimination of a proton from one of the carried methyl groups , the elimination (E2) for 2-methyl propene (isobutylene).
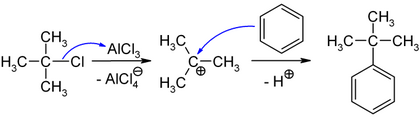
Under the action of anhydrous Lewis acids , such as. B. aluminum chloride or iron (III) chloride , it comes with elimination of a chloride ion to the formation of the tert-butyl cation, which can act as an electrophile alkylating.
Tert reacts with water. Butyl chloride slowly hydrolytically in a nucleophilic substitution ( S N 1 reaction ) with the formation of tert. Butanol , hydrogen ions and chloride ions . This reaction can be followed by measuring the conductivity , since the concentration of the ions formed increases more and more and the concentration of tert. Butyl chloride decreases. The evaluation of this measurement shows that there is a 1st order reaction.
Safety-related parameters
2-chloro-2-methylpropane forms highly flammable vapor-air mixtures. The compound has a flash point of approx. −33 ° C. The explosion range is between 1.8 vol.% As the lower explosion limit (LEL) and 10.1 vol.% As the upper explosion limit (UEL). The ignition temperature is 570 ° C. The substance therefore falls into temperature class T1.
use
In organochemical synthesis, 2-chloro-2-methylpropane is used to introduce a tert-butyl group into organic molecules. The compound is used as an electrophile in Friedel-Crafts alkylations in order to bind a tert-butyl radical to an aromatic . Starting from benzene, catalysis with anhydrous aluminum chloride enables the preparation of tert- butylbenzene .
The initially formed tetrachloroaluminate ion reacts with the proton split off from the aromatic to form hydrogen chloride with regression of the aluminum chloride, so that only substoichiometric amounts of AlCl 3 are required.
safety instructions
2-chloro-2-methylpropane is highly volatile and highly flammable. Therefore, you must always work under a well-pulling fume cupboard. A safety goggles must be worn at work always. When decanting, measures must be taken against static charging.
- In the event of inhalation: remove affected person to fresh air immediately.
- In case of skin contact: wash off with plenty of water.
- In the event of eye contact: rinse thoroughly with water for at least 15 minutes ( eye shower ). Possibly. consult an ophthalmologist.
- If swallowed: do not induce vomiting if possible.
- Take off or remove contaminated clothing immediately.
Chronic contact with the substance can cause liver and kidney damage.
Web links
- Acros 2-chloro-2-methylpropane data sheet , accessed February 26, 2010.
- Data sheet 2-chloro-2-methylpropane (PDF) from Merck , accessed on February 26, 2010.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Entry on tert-butyl chloride in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on March 14, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-106.
- ↑ HPA Groll, G. Hearne, FF Rust, WE Vaughan: HALOGENATION OF HYDROCARBONS Chlorination of Olefins and Olefin-Paraffin Mixtures at Moderate Temperatures; Induced Substitution , in: Ind. Eng. Chem. , 1939 , 31 (10), pp. 1239-1244; doi: 10.1021 / ie50358a017 .
- ↑ Jansen / Ralle / Peper: reaction kinetics and chemical equilibrium , Aulis Verlag, Cologne 1984, ISBN 3-7614-0642-8 .
- ^ E. Brandes, W. Möller: Safety-related parameters - Volume 1: Flammable liquids and gases , Wirtschaftsverlag NW - Verlag für neue Wissenschaft GmbH, Bremerhaven 2003.
- ↑ Entry on butyl chloride. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on March 14, 2018.