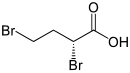
2,4-dibromobutyric acid
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||
| ( S ) - (left) or ( R ) -2,4-dibromobutanoic acid | |||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | 2,4-dibromobutyric acid | ||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 4 H 6 Br 2 O 2 | ||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid |
||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 245.8 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||
| Melting point |
28 ° C |
||||||||||||
| boiling point |
131 ° C (33 h Pa ) |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
2,4-Dibromobutanoic acid is a chemical compound that belongs to the halogenated aliphatic carboxylic acids and the bromobutanoic acids . It is primarily used as an intermediate in the pharmaceutical industry and for the synthesis of fine chemicals .
synthesis
2,4-Dibromobutanoic acid can be produced by reacting cyclopropanecarboxylic acid with elemental bromine .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d 2,4-Dibromobutyric acid (Chemada) ( Memento from November 13, 2007 in the Internet Archive ).
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ BH Nicolet, L. Sattler: A suggested mechanism of the splitting of the cyclopropane ring by bromine , in: J. Am. Chem. Soc. , 1927 , 49 (8) , pp. 2066-2071; doi: 10.1021 / ja01407a035 .
