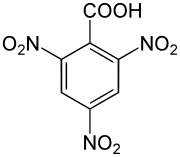
2,4,6-trinitrobenzoic acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 2,4,6-trinitrobenzoic acid | |||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 3 N 3 O 8 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
orthorhombic crystals |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 257.12 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
228.7 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
0.65 (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
Slightly soluble in water and benzene , very soluble in ethanol , soluble in diethyl ether and acetone |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
The 2,4,6-trinitrobenzoic is an explosive solid. It is derived from both benzoic acid and nitrobenzene . The structure consists of a benzene ring with an attached carboxy group (-COOH) and three nitro groups (-NO 2 ) as substituents .
presentation
It is made from 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) by oxidation with sodium dichromate and sulfuric acid . Nitric acid , nitric acid potassium chlorate solution or chromosulfuric acid can also be used as oxidizing agents .
A decarboxylation in boiling water leads to trinitrobenzene .
properties
The 2,4,6-trinitrobenzoic acid forms yellow, needle-shaped crystals. Due to the −M effect of the three nitro groups, it has a significantly higher acidity compared to benzoic acid, nitrobenzoic acids and 3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid . The pK s value (0.65) is therefore correspondingly lower (benzoic acid: 4.20).
Explosion parameters
2,4,6-trinitrobenzoic acid is an explosive substance. It is included in the list of explosive substances in accordance with Section 2 (6) of the Explosives Act (list of old substances). Important explosion indicators are:
- Heat of explosion : 2894 kJ kg −1 (H 2 O (g))
- Normal gas volume : 872 l kg −1
- Specific energy : 871 kJ kg −1
- Steel sleeve test : limit diameter 2 mm
- Lead block bulge : 28.3 cm 3 g −1
- Impact sensitivity : 10 Nm
- Sensitivity to friction : no reaction up to 353 N pin load
safety instructions
At 190 ° C an exothermic pre-reaction (decarboxylation) takes place with the release of carbon dioxide to form trinitrobenzene. With heavy metals, explosive salts are formed that are sensitive to heat and shock.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-510.
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry for CAS no. 129-66-8 in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on March 7, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b CRC Handbook of Tables for Organic Compound Identification , Third Edition, 1984, ISBN 0-8493-0303-6 .
- ↑ HT Clarke, WW Hartman: 2,4,6-Trinitrobenzoic Acid In: Organic Syntheses . 2, 1922, p. 95, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.002.0095 ; Coll. Vol. 1, 1941, p. 543 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Koehler, J .; Meyer, R .; Homburg, A .: Explosivstoffe , tenth, completely revised edition, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2008, ISBN 978-3-527-32009-7 .
- ↑ HT Clarke, WW Hartman: 1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene In: Organic Syntheses . 2, 1922, p. 93, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.002.0093 ; Coll. Vol. 1, 1941, p. 541 ( PDF ).
