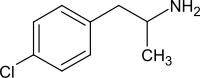
4-chloramphetamine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | 4-chloramphetamine | |||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 9 H 12 Cl N | |||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 169.65 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
4-chloramphetamine ( 4-CA ), also known as para- chloramphetamine ( PCA ), is an amphetamine derivative and causes the release of the monoaminergic neurotransmitters serotonin , dopamine and noradrenaline , similar to MDMA . However, it has a significantly higher neurotoxicity . This can be attributed to the almost unrestrained release of dopamine and serotonin compared to MDMA. It is used by neuroscientists to selectively kill serotonin neurons in the brain for research purposes, just as 6-hydroxydopamine is used to destroy dopamine and norepinephrine neurons.
4-chloramphetamine has been clinically studied for use as an antidepressant and has been well tolerated. However, a neurotoxic effect found in animal experiments discouraged further research activities in this indication.
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ MP Johnson, XM Huang, R. Oberlender, JF Nash, DE Nichols: Behavioral, biochemical and neurotoxicological actions of the alpha-ethyl homologue of p-chloroamphetamine. In: European Journal of Pharmacology . 191 (1), Nov 20, 1990, pp. 1-10. PMID 1982656
- ↑ EM Gal, PA Christiansen, LM Younger: Effect of p-chloroamphetamine on cerebral tryptophan-5-hydroxylase in vivo: a reexamination. In: Neuropharmacology . 14 (1), Jan 1975, pp. 31-39. PMID 125387
- ↑ G. Curzon, JC Fernando, CA Marsden: 5-Hydroxytryptamine: the effects of impaired synthesis on its metabolism and release in rat. In: British Journal of Pharmacology . 63 (4), Aug 1978, pp. 627-634. PMID 80243
- ↑ MI Colado, TK Murray, AR Green: 5-HT loss in rat brain following 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), p-chloroamphetamine and fenfluramine administration and effects of chlormethiazole and dizocilpine. In: British Journal of Pharmacology. 108 (3), Mar 1993, pp. 583-589. PMID 7682129
- ↑ U. Freo, P. Pietrini, G. Pizzolato, M. Furey, A. Merico, S. Ruggero, M. Dam, L. Battistin: Cerebral metabolic responses to clomipramine are greatly reduced following pretreatment with the specific serotonin neurotoxin para- chloroamphetamine (PCA). A 2-deoxyglucose study in rats. In: Neuropsychopharmacology . 13 (3), Nov 1995, pp. 215-222. PMID 8602894
- ^ AT Shulgin: Psychotomimetic Drugs: Structure-Activity Relationships. In: Leslie L. Iversen, Susan D. Iversen, Solomon H. Snyder (Eds.): Handbook of Psychopharmacology. Volume 11: Stimulants. Plenum Press, New York 1978, chapter 6.