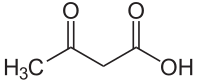
Acetoacetic acid
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Acetoacetic acid | ||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 4 H 6 O 3 | ||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 102.09 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid or solid |
||||||||||||
| Melting point |
36–37 ° C or viscous liquid at room temperature |
||||||||||||
| solubility |
miscible with water |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Acetoacetic acid is the common name of 3-oxobutanoic acid . The anion of the acid is called acetoacetate or acetoacetate .
Extraction and presentation
Acetoacetic acid is produced by saponification ( hydrolysis ) of ethyl acetoacetate and subsequent reaction with acids . Another way of representing it is the oxidation of butyric acid with hydrogen peroxide .
In the reaction of ethyl acetate with sodium , a Claisen condensation produces ethyl acetoacetate, which can be converted into the pure acid by ester cleavage .
properties
In the case of acetoacetic acid, there is a keto-enol tautomerism . As a result of the inductive effect of the keto group, acetoacetic acid reacts more acidic than the butyric acid on which it is based .
With elemental chlorine or bromine , acetoacetic acid decomposes into carbon dioxide , the corresponding hydrogen halide and chloroacetone or bromoacetone .
use
Pure acetoacetic acid is rarely used because it decomposes easily with decarboxylation into carbon dioxide and acetone (rapidly at 100 ° C). Their esters and salts are more important .
Biological importance
Acetoacetic acid (acetoacetate), like its isomer 2-oxobutanoic acid , occurs as an intermediate product in the metabolism , is one of the keto bodies and is of particular importance in catabolism in hunger or diet. Acetyl-CoA produced in a state of hunger is converted into acetoacetate via an intermediate product (3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry on acetoacetic acid. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 15, 2014.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ A b F. Beilstein: Handbook of organic chemistry , 3rd edition, 1st volume. Verlag Leopold Voss, 1893. S. 591. Full text
- ↑ R. Otto: Analogies between ketonic acids and alkylsulfonated fatty acids in reports of the German chemical society 1888 , 21 , pp. 89-94. Full text
literature
- Beilstein E III 3; 1178
- Horton Robert, biochemistry; P. 687


