Ajmaline
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
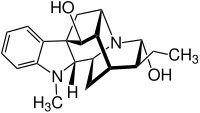
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Ajmaline | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
(17 R ) -17.21 α- Ajmalanediol |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 20 H 26 N 2 O 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action |
Blockage of sodium channels |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 326.43 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Ajmaline is an indole alkaloid from the roots of the Indian snake root ( Rauwolfia serpentina ). It is used as a drug to treat cardiac arrhythmias .
Occurrence and extraction
Ajmaline is obtained from the dried roots of the Indian snake root ( Rauwolfia serpentina ).
effect
Ajmaline is an active ingredient in the class I antiarrhythmic group . As a sodium channel blocker with a prolonging effect on the duration of the action potential, it is included in class Ia of the Vaughan-Williams classification . Ajmaline inhibits the rapid sodium current in the heart muscle cells and reduces the speed of depolarization during phase 0 of the action potential .
Pharmacokinetics
Ajmaline is only given by intravenous injection. It has a very short, redistribution-related initial plasma half-life of 12 to 15 minutes. The elimination takes place at 90 percent hepatic . The remaining 10 percent are eliminated through the kidneys .
application
Supraventricular tachycardias ( e.g. AV-junctional tachycardias, supraventricular tachycardias in WPW syndrome , paroxysmal atrial fibrillation ), if they are symptomatic and require treatment, life-threatening ventricular tachycardias .
Contraindications and warnings
In the case of manifest heart failure , significant electrolyte disturbance or pronounced hypotension as well as overdosage of digitalis , ajmaline must not be used, in severe bradycardia , SA blockages and high-grade AV blockages and sinus node syndrome only if a pacemaker is implanted. If the heart's pumping function is restricted (ejection fraction <35 percent) and in the first three months after a heart attack , it may only be used in the case of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias.
If the liver or kidney function is impaired , the dose must be adjusted. Renal function should be monitored during therapy.
possible side effects
Particularly feared are the paradoxical proarrhythmic effects of ajmaline, which can occur particularly in patients with coronary artery disease . Seizures and very rarely changes in the blood count can occur.
Finished medicinal products
Gilurytmal ® (D: Carinopharm ; A: Pharmaselect Handels GmbH)
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Ajmaline data sheet at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 20, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ^ Eduard Burgis intensive course in general and special pharmacology , 2nd edition, Urban & Fischer, 2002 , ISBN 3-437-42611-7 .
