Antimycins
The antimycins are a group of several closely related antibiotics from streptomycetes . As antimycin A refers to a mixture of different antimycins, the main components of the antimycins A 1 , A 2 , A 3 and A 4 are.
The antimycins act as an inhibitor of the respiratory chain .
Extraction and presentation
Antimycin A can be extracted from Streptomyces antibioticus cultures which are cultivated with an initial pH of 6.8 to 7.1, without iron supplementation and with 2 g DL - tryptophan . The individual representatives can be isolated by HPLC .
Representative
| Surname | Antimycin A 1 | Antimycin A 2 | Antimycin A 3 | Antimycin A 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structural formula |
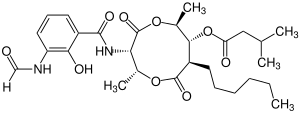
|

|

|

|
| IUPAC name | [(2 R , 3 S , 6 S , 7 R , 8 R ) -3 - [(3-Formamido-2-hydroxybenzoyl) amino] -8-hexyl-2,6-dimethyl-4,9-dioxo-1 , 5-dioxonan-7-yl] -3-methylbutanoate | [3 - [(3-Formamido-2-hydroxybenzoyl) amino] -8-hexyl-2,6-dimethyl-4,9-dioxo-1,5-dioxonan-7-yl] butanoate | [(2 R , 3 S , 6 S , 7 R , 8 R ) -8-butyl-3 - [(3-formamido-2-hydroxybenzoyl) amino] -2,6-dimethyl-4,9-dioxo-1 , 5-dioxonan-7-yl] -3-methylbutanoate | [8-Butyl-3 - [(3-formamido-2-hydroxybenzoyl) amino] -2,6-dimethyl-4,9-dioxo-1,5-dioxonan-7-yl] butanoate |
| German name | 3-methylbutanoic acid 3 - ((3- (formylamino) -2-hydroxybenzoyl) amino) -8-hexyl-2,6-dimethyl-4,9-dioxo-1,5-dioxonan-7-yl ester | |||
| synonym | Fintrol | Blastmycin | ||
| CAS number | 642-15-9 | 27220-57-1 | 522-70-3 | 27220-59-3 |
| 1397-94-0 | ||||
| PubChem | 12550 | 3084471 | 245869 | 3084472 |
| Molecular formula | C 28 H 40 N 2 O 9 | C 27 H 38 N 2 O 9 | C 27 H 38 N 2 O 9 | C 25 H 34 N 2 O 9 |
| Molar mass | 548.63 g mol −1 | 534.61 g mol −1 | 520.58 g mol −1 | 506.55 g mol −1 |
| Melting point | 149-150 ° C | 174-175 ° C | ||
Properties and effects
| safety instructions | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surname |
Antimycin A |
|||||||
| CAS number |
1397-94-0 |
|||||||
|
||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||
The antimycins form colorless crystals that are almost insoluble in water but soluble in ethanol , acetone and diethyl ether .
Antimycin A binds to the Q i site in the cytochrome bc 1 complex and thus prevents electron transfer from heme b H to ubiquinone .
It binds to complex III and thus blocks the transfer of electrons from coenzyme Q to cytochrome c . The components of the respiratory chain that lie in front of the site of action of antimycin A in complex III remain reduced. All components behind it remain oxidized. Thus, the consumption of is oxygen in the complex IV and the synthesis of ATP in the complex V inhibited.
Individual evidence
- ^ N. Neft, TM Farley: Conditions Influencing Antimycin Production by a Streptomyces Species Grown in Chemically Defined Medium . In: Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy . tape 1 , no. 3 , March 1, 1972, p. 274 , doi : 10.1128 / aac.1.3.274 (English, PDF ).
- ↑ Steven TK Ha, Charles L. Wilkins, Sharon L. Abidi: Analysis of antimycin A by reversed-phase liquid chromatography / nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry . In: Analytical Chemistry . tape 61 , no. 5 , March 1989, pp. 404-408 , doi : 10.1021 / ac00180a005 .
- ↑ a b Entry on Antimycin A in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 6, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d C. Vézina: Antimycin A, a teleocidal antibiotic. In: Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy . Volume 6, 1966, pp. 757-766, PMID 5985309 .
- ↑ a b c Entry on Antimycins. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on December 29, 2014.

