Aprepitant
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
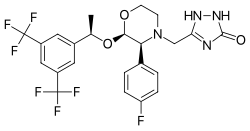
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Aprepitant | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
5 - [((2 S , 3 R ) -2 - {(1 R ) -1- [3,5-bis (trifluoromethyl) phenyl] ethoxy} -3- (4-fluorophenyl) morpholin-4-yl) methyl] -1,2-dihydro-1,2,4-triazol-3-one |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 23 H 21 F 7 N 4 O 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | |||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 534.43 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
252.9 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Aprepitant (trade name: Emend, manufactured by MSD Sharp & Dohme ) is a drug from the group of neurokinin -1 receptor - antagonist ( NK-1 receptor antagonists ) that serves as an antiemetic for the prevention of acute and delayed nausea and vomiting associated with highly emetogenic chemotherapy used becomes.
Clinical information
Application areas (indications)
Aprepitant is approved for the prevention of nausea and vomiting after chemotherapy and after operations ( postoperative nausea and vomiting , PONV). Here, aprepitant is often used in combination with 5-HT3 antagonists and glucocorticoids , as it is only officially approved in combination with these substances. Aprepitant is available in the form of hard capsules containing 40 mg (PONV), 80 and 125 mg (chemotherapy) and in intravenous form (trade name Ivemend).
Side effects
The side effects include malaise, loss of appetite, tiredness, headache, liver involvement (increased transaminases ).
Contraindications
Aprepitant must not be given if you are known to be hypersensitive to the active ingredient. It must also not be taken during pregnancy. Treatment with aprepitant is not recommended during breastfeeding.
Drug interactions
Aprepitant shows a number of interactions with other medicinal products that should be considered when using it. Drugs that are also metabolized via CYP3A4, or that inhibit or induce them, are particularly problematic. For example, aprepitant should not be given in combination with terfenadine .
Pharmacological properties
Mechanism of action (pharmacodynamics)
Aprepitant acts as an antagonist of the neurokinin receptor NK1, by preventing the binding of natural ligands for NK1, substance P prevented. The binding of substance P to the NK1 receptor, which is located on cells in the vomiting center in the brain stem , triggers the nausea; this is reduced by aprepitant.
In addition to aprepitant, there is another substance with this mechanism of action, the drug fosaprepitant , a prodrug of aprepitant. Fosaprepitant is approved for use by infusion in medicinal products under the trade name Ivemend.
Absorption and distribution in the body (pharmacokinetics)
Aprepitant is primarily metabolized via CYP3A4 . The drug is both a moderate inhibitor and inducer of cytochrome .
Web links
- Public Assessment Report (EPAR) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for: Aprepitant
- Aprepitant - antiemetic of a new class (PZ)
- Neurokinin receptor antagonists (ÖAZ) ( Memento from June 18, 2009 in the Internet Archive )
- Infomed pharma criticism entry aprepitant
Individual evidence
- ↑ Sara BE Andersson, Caroline Alvebratt, Christel AS Bergström: Controlled Suspensions Enable Rapid Determinations of Intrinsic Dissolution Rate and Apparent Solubility of Poorly Water-Soluble Compounds in Pharm. Res. 39 (2017) 1805-1816, doi : 10.1007 / s11095-017 -2188-1 .
- ↑ There is not yet a harmonized classification for this substance . A label of 3 - [[(2R, 3S) -2 - [(1R) -1- [3,5-bis (trifluoromethyl) phenyl] ethoxy) -3- (4-fluorophenyl) derived from a self-classification by the distributor is shown ) morpholino] methyl] -1H-1,2,4-triazol-5 (4H) -one in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on December 17, 2019.
- ↑ Red List Online, as of August 2009.
- ↑ Swiss Medicines Compendium , as of August 2009.
- ↑ AGES-PharmMed, as of August 2009.