Arndt-Eistert homologation
The Arndt-Eistert homologation or Arndt-Eistert synthesis is a reaction from the field of organic chemistry . A carboxylic acid is extended ( homologated ) by a methylene group (–CH 2 -) in three stages . The third stage is also known as the Wolff rearrangement .
The reaction is named after its discoverers, the chemists Fritz Arndt (1885–1969) and Bernd Eistert (1902–1978).
Overview
In the first stage the carboxylic acid is converted into the corresponding acid chloride . This is followed by the addition of the methylene group, which is provided by the diazomethane . An α-diazo methyl ketone is formed. The third stage, the Wolff rearrangement , leads with z. B. silver oxide as a catalyst and water to form the homologous carboxylic acid. However, by exchanging water for other compounds, other derivatives can also be formed (see below).
In practice, the reaction is carried out with an additional equivalent of diazomethane , since the HCl molecule which is split off can add to the diazoketone and produce an α-halo-ketone ( kidney stone reaction ). The additional equivalent of diazomethane converts HCl into chloromethane , which is no longer reactive enough.
mechanism
The acid chloride 2 is first formed from the carboxylic acid 1 . The nucleophilic addition of the methylene group of the diazomethane then takes place at its terminal carbon atom. This creates a diazonium betaine 3 in a transition state , which converts into the mesomeric-stabilized diazoketone 4 with elimination of HCl ( addition - elimination mechanism).
At elevated temperatures, diazo ketones can split off molecular nitrogen with silver and copper catalysts while taking the binding electrons with them . The intermediate is a classic carbene 5 . In the next step, a Wolff rearrangement takes place, so that the ketene 6 is formed. This reacts with water in a nucleophilic addition to the carboxylic acid 7 .
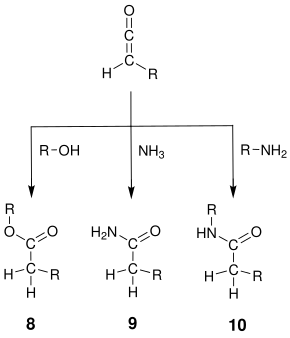
The ketene 6 can also be reacted with other H-acidic, nucleophilic compounds in a nucleophilic addition :
If an alcohol is used instead of water , the corresponding ester 8 is obtained . The addition of ammonia or amines to amides 9 and 10 are obtained.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c L. Kürti , B. Czakó: Stratigic Applications of Named Reactions in Organic Synthesis . Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam 2005, ISBN 978-0-12-429785-2 , p. 18.
- ↑ T. Laue, A. Plagens: Name and keyword reactions . 5th edition. BG Teubner Verlag / GWV Fachverlage, Wiesbaden 2006, ISBN 978-3-8351-0091-6 , p. 17.
literature
- Hans Beyer , Wolfgang Walter : Textbook of organic chemistry . 23. revised and updated edition. S. Hirzel, Stuttgart / Leipzig 1998, ISBN 3-7776-0808-4 .