Atosiban
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
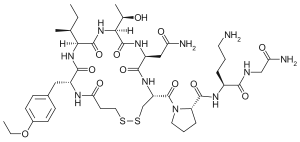
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Atosiban | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
1- (3-sulfanylpropionyl) -2- (4-ethoxyphenyl- D -alanyl) -4- L -threonine-8- L -ornithinoxytocin ( IUPAC ) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 43 H 67 N 11 O 12 S 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
Solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | |||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 994.19 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
in water ≤100 mg / mL at 20 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Atosiban is a drug from the group of tocolytics that is used to suppress labor ( tocolysis ). This makes it an alternative to fenoterol and nifedipine (off label).
Clinical information
Application areas (indications)
The active ingredient atosiban is indicated to delay the threat of premature birth in pregnant women if the following criteria are met:
- Regular uterine contractions lasting at least 30 seconds and a frequency of ≥ 4 per 30 minutes.
- Opening of the cervix to a width of 1–3 cm (0–3 in primiparous women ) and cervical narrowing ≥ 50%.
- Age ≥ 18 years.
- Pregnancy in the 24th – 33rd completed week of pregnancy .
- Normal heart rate of the fetus.
Contraindications (contraindications)
The active ingredient must not be used in people who may be hypersensitive (allergic) to atosiban. In women before the 24th or after the 33rd week of pregnancy or women with premature rupture of the bladder , bleeding from the uterus, eclampsia (dangerous disease at the end of pregnancy caused by toxins in the blood), preeclampsia (disease that leads to eclampsia may) or problems with the placenta, atosiban must also not be used.
Pharmacological properties
Mechanism of action (pharmacodynamics)
Atosiban is a competitive antagonist at the oxytocin receptor. Atosiban's potency on the human oxytocin receptor is less than that of oxytocin and it is not selective. After bonding, the frequency of contraction and the tone of the uterine muscles are lowered, resulting in a suppression of labor. Atosiban binds with greater affinity to the human vasopressin V1a receptor, where it inhibits the action of vasopressin . Atosiban thus counteracts labor and ensures that the uterus is immobilized. In comparative studies with β-sympathomimetics , atosiban showed comparable effects, although no cardiovascular effects were observed. With the recommended dosage, immobilization can be achieved for up to 12 hours.
Chemical-pharmaceutical information
Atosiban is the international non-proprietary name (INN) for 1- (3-mercaptopropionyl) -2- (d-4-ethoxyphenylalanyl) -4-l-threonine-8-l-ornithine oxytocin - a synthetic structure analogue of the body's own neuropeptide oxytocin - and is administered parenterally as atosiban acetate .
Finished medicinal products
Tractocile ( Ferring )
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c data sheet atosiban from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on June 15, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c Tractocile: Summary of Product Characteristics, as of May 19, 2009 on the website of the European Medicines Agency EMEA (PDF, 257 kB), accessed on August 30, 2009.
- ↑ W. Forth, D. Henschler, W. Rummel: General and special pharmacology and toxicology . 9th edition. URBAN & FISCHER, Munich 2005, ISBN 3-437-42521-8 .
- ↑ Papatsonis D, Flenady V, Cole S, Liley H: Oxytocin receptor antagonists for inhibiting preterm labor . In: Cochrane database of systematic reviews (online) . No. 3, 2005, p. CD004452. doi : 10.1002 / 14651858.CD004452.pub2 . PMID 16034931 .