Benzyl group
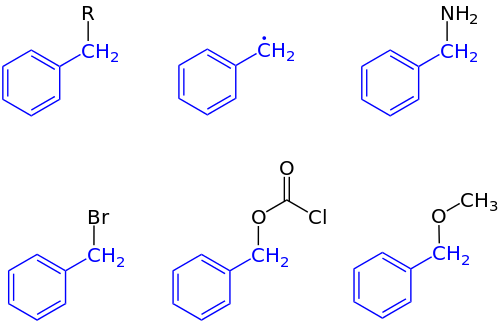
In organic chemistry, the benzyl group , older α-tolyl group , is the phenylmethylene group –CH 2 -C 6 H 5 ; The following abbreviations, some of which are ambiguous and are not regulated by any IUPAC guideline, are used for benzyl : Bn (also stands for the benzylidene group ), Bz (also stands for the benzoyl group), more rarely the unequivocal abbreviations Bzl or CH 2 Ph . Examples of compounds having a benzyl group areBenzyl alcohol , benzylamine , benzyl chloride and the benzyl butyl phthalate (BBP) used as a plasticizer .
The benzyl group is used in peptide chemistry, carbohydrate chemistry and in many total syntheses of natural products as a protective group for heteroatoms because it can easily be split off again hydrogenolytically , ie under mild conditions. The only by-product is volatile toluene .
The benzylation , ie introduction of a benzyl group in a compound is usually by a substitution reaction with benzyl halides.
literature
- Philip J. Kocieński: Protecting Groups. Thieme, Stuttgart / New York 1994, ISBN 3-13-135601-4 .
See also
- Benzyloxycarbonyl protecting group (Z- / Cbz-): benzyl chloroformate